Java 生态系统概述
Table of Contents
- Introduction
-
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
-
Architecture of the JVM
- Class Loader
-
JVM Memory
- Method Area
- Heap
- Stack Area
- Program Counter (PC) Register
- Native Method Stack
-
Execution Engine
- Interpreter
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Compiler
- Garbage Collector
-
Architecture of the JVM
-
JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
-
Key Components of the JRE
- Execution Tasks
- Class Libraries
- Java Native Interface (JNI)
- Security Manager
-
Key Components of the JRE
-
JDK (Java Development Kit)
-
Core Features of the JDK
- javac (Java Compiler)
- java (Java Application Launcher)
- jdb (Java Debugger)
- jar (Java Archive Tool)
- javadoc (Java Documentation Generator)
-
Core Features of the JDK
- JVM vs JRE vs JDK: What's the Difference?
- JDK, JRE, JVM Hierarchy
Introduction
The Java ecosystem is the broad set of tools, technologies, libraries, and frameworks that surround and support the Java programming language. It encompasses everything needed to develop, deploy, and manage Java applications. It revolves around JDK, JRE, JVM
JVM (Java Development Kit)
The JVM acts like a translator that allows your computer to run Java programs and other languages compiled into Java bytecode. It translates the code into something your computer's hardware can understand and execute.
Architecture of the JVM
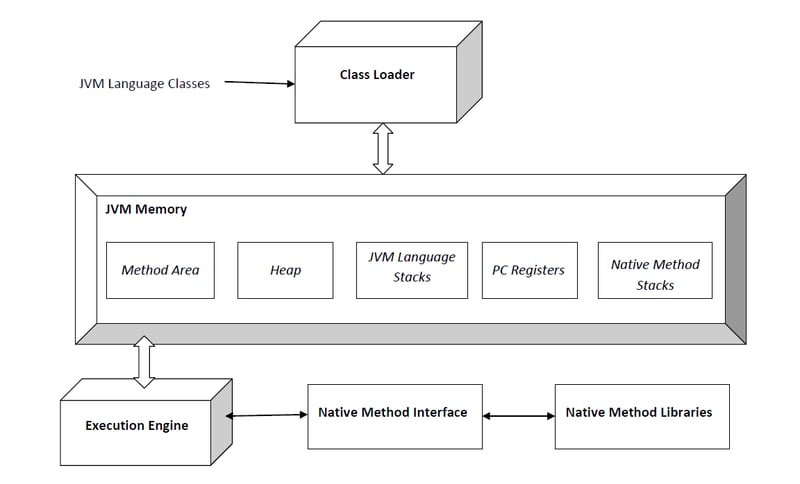
Class Loader
Loading load
Load .class files into memory. Locates, loads, and links class files (Java bytecode) for execution.-
Linking
- Verification: Verifies the bytecode.
- Preparation: Allocates memory for static variables and initializes the memory to default values.
- Resolution: Resolves symbolic references to direct references.
Initialization
Initialization is the final step where the JVM prepares a class or interface for use. This step happens after the class has been loaded (into memory) and linked.
JVM Memory
-
Method Area
Method area Stores class-level data such as methods and variables, the runtime constant pool, and code for methods.
public class Person { private String name; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }When you define a class Person, the Method Area stores the structure of the Person class, including its methods (setName) and fields (name), and the runtime constant pool which contains references like method names and constant values.
-
Heap
Heap is where the runtime memory objects are allocated. The heap is shared among all threads and is where the garbage collection process occurs.
Person p = new Person();
When you create a new Person object, it is allocated on the Heap.
-
Stack Area
Stack area stores frames, which contain local variables, operand stacks, and references to the runtime constant pool of the class being executed. Each thread has its own stack.
public void someMethod() { int a = 10; int b = 20; int sum = a b; }Each time someMethod is called, a new frame is pushed onto the Stack Area. This frame includes local variables (a, b, and sum), an operand stack for intermediate calculations, and a reference to the method’s class in the Runtime Constant Pool.
Program Counter (PC) Register
PC contains the address of the current JVM instruction being executed. Each thread has its own PC register.Native Method Stack
Similar to the Java stack, but used for native methods.
Execution Engine
Interpreter
Interpreter reads Java bytecode and executes it line by line, converting each bytecode instruction into a sequence of machine-level instructions that can be executed by the CPU.Just-In-Time (JIT) Compiler
Converts bytecode into native machine code at runtime to improve performance.Garbage Collector
Garbage collector is responsible for automatically managing memory in the JVM. It identifies and deallocates memory that is no longer in use, freeing it up for new objects.
JRE
JRE is a software package that provides the necessary environment to run Java applications. It is designed to execute Java bytecode on a machine, making it an essential part of the "write once, run anywhere" (WORA) principle of Java.
Key Components of the JRE
Execution Tasks
The JRE facilitates the execution of Java applications by providing the JVM and the necessary libraries and resources. JRE ensures that the JVM has everything it needs to perform these tasks on any platform. Think of the JRE as the complete package that includes the JVM, which does the heavy lifting, and other components that support the execution of Java applications.Class Libraries
JRE includes a set of standard Java class libraries, which provide reusable code for performing common tasks, like data structures, I/O, networking, concurrency, and more.Java Native Interface (JNI)
JNI allows Java applications to interact with native code written in languages like C or C . This feature is essential for integrating platform-specific features or using existing native libraries.Security Manager
The Security Manager enforces security policies for Java applications, restricting actions such as file access, network connections, and the execution of potentially unsafe code.
JDK (Java Development Kit)
JDK is a tools that enables developers to write, compile, debug, and run Java applications. It is a superset of JRE and includes additional tools for Java development.
Core Features of the JDK
javac (Java Compiler)
javac is use to for converting Java source code (.java files) into bytecode (.class files). This bytecode is then executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).java (Java Application Launcher)
java command launches a Java application. It loads the necessary class files, interprets the bytecode, and starts the application.jdb (Java Debugger)
jdb is the command-line debugger for Java programs. It allows you to inspect and debug Java applications at runtime.jar (Java Archive Tool)
jar tool packages multiple files into a single archive file, typically with a .jar extension. These JAR files are used to distribute Java applications and libraries.javadoc (Java Documentation Generator)
javadoc generates HTML documentation from Java source code, using the special /** */ comments known as doc comments.
JVM vs JVE vs JDK, what's the difference?
| Feature/Aspect | JVM | JRE | JDK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Executes Java bytecode | Provides the environment to run Java applications | Provides tools to develop, compile, debug, and run Java applications |
| Includes | JVM itself, which includes class loader, bytecode verifier, and execution engine | JVM Core libraries (like java.lang, java.util, etc.), and other runtime components | JRE Development tools (like javac, jdb, jar, etc.), documentation |
| Components | - Class Loader - Bytecode Verifier - Execution Engine (Interpreter, JIT) |
- JVM - Core Java libraries - Java Plug-in - Java Web Start |
- JRE - Java Compiler (javac) - JAR Tool (jar) - Debugger (jdb) - Documentation Generator (javadoc) - Other development tools |
| Main Functionality | Executes Java bytecode, enabling platform independence | Provides the minimum requirements to run Java applications | Allows developers to write, compile, and debug Java code |
| Who Uses It? | End-users running Java applications | End-users running Java applications | Java developers writing and compiling Java applications |
| Installation Size | Smallest | Larger than JVM but smaller than JDK | Largest (includes JRE and development tools) |
| Developer Tools | No | No | Yes (includes compiler, debugger, profiler, etc.) |
| Required to Run Java Programs | Yes | Yes | No (but needed to create Java programs) |
| Platform Independence | Provides platform independence by abstracting the underlying hardware | Yes, because it includes the JVM | Yes, it includes everything from JRE |
| Examples of Usage | - Running any Java application (e.g., desktop applications, servers) | - Running Java applications in production or end-user environments | - Writing and compiling Java code - Packaging applications - Debugging |
| Availability | Part of JRE and JDK | Standalone or part of JDK | Standalone package |
JDK, JRE, JVM hierarchy
JDK (Java Development Kit) │ ├── JRE (Java Runtime Environment) │ │ │ ├── JVM (Java Virtual Machine) │ │ ├── Class Loader │ │ ├── Bytecode Verifier │ │ ├── Execution Engine │ │ │ ├── Interpreter │ │ │ ├── Just-In-Time (JIT) Compiler │ │ │ └── Garbage Collector │ │ └── Runtime Libraries (core libraries like java.lang, java.util, etc.) │ │ │ └── Java APIs (Core libraries and additional libraries) │ ├── Development Tools (like javac, jdb, jar, javadoc, etc.) └── Documentation (API docs, guides)
-
 在细胞编辑后,如何维护自定义的JTable细胞渲染?在JTable中维护jtable单元格渲染后,在JTable中,在JTable中实现自定义单元格渲染和编辑功能可以增强用户体验。但是,至关重要的是要确保即使在编辑操作后也保留所需的格式。在设置用于格式化“价格”列的“价格”列,用户遇到的数字格式丢失的“价格”列的“价格”之后,问题在设置自定义单元格...编程 发布于2025-06-25
在细胞编辑后,如何维护自定义的JTable细胞渲染?在JTable中维护jtable单元格渲染后,在JTable中,在JTable中实现自定义单元格渲染和编辑功能可以增强用户体验。但是,至关重要的是要确保即使在编辑操作后也保留所需的格式。在设置用于格式化“价格”列的“价格”列,用户遇到的数字格式丢失的“价格”列的“价格”之后,问题在设置自定义单元格...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-06-25
MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 CSS可以根据任何属性值来定位HTML元素吗?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何属性值,在CSS中,可以基于特定属性(如下所示)基于特定属性的基于特定属性的emants目标元素: 字体家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出现一个常见的问题:元素可以根据任何属性值而定位吗?本文探讨了此主题。的目标元素有任何任何属性值,属...编程 发布于2025-06-25
CSS可以根据任何属性值来定位HTML元素吗?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何属性值,在CSS中,可以基于特定属性(如下所示)基于特定属性的基于特定属性的emants目标元素: 字体家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出现一个常见的问题:元素可以根据任何属性值而定位吗?本文探讨了此主题。的目标元素有任何任何属性值,属...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 为什么HTML无法打印页码及解决方案无法在html页面上打印页码? @page规则在@Media内部和外部都无济于事。 HTML:Customization:@page { margin: 10%; @top-center { font-family: sans-serif; font-weight: bo...编程 发布于2025-06-25
为什么HTML无法打印页码及解决方案无法在html页面上打印页码? @page规则在@Media内部和外部都无济于事。 HTML:Customization:@page { margin: 10%; @top-center { font-family: sans-serif; font-weight: bo...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 Python读取CSV文件UnicodeDecodeError终极解决方法在试图使用已内置的CSV模块读取Python中时,CSV文件中的Unicode Decode Decode Decode Decode decode Error读取,您可能会遇到错误的错误:无法解码字节 在位置2-3中:截断\ uxxxxxxxx逃脱当CSV文件包含特殊字符或Unicode的路径逃...编程 发布于2025-06-25
Python读取CSV文件UnicodeDecodeError终极解决方法在试图使用已内置的CSV模块读取Python中时,CSV文件中的Unicode Decode Decode Decode Decode decode Error读取,您可能会遇到错误的错误:无法解码字节 在位置2-3中:截断\ uxxxxxxxx逃脱当CSV文件包含特殊字符或Unicode的路径逃...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 如何为PostgreSQL中的每个唯一标识符有效地检索最后一行?postgresql:为每个唯一标识符提取最后一行,在Postgresql中,您可能需要遇到与在数据库中的每个不同标识相关的信息中提取信息的情况。考虑以下数据:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在数据集中的每个唯一ID中检索最后一行的信息,您可以在操作员上使用Postgres的有效效率: ...编程 发布于2025-06-25
如何为PostgreSQL中的每个唯一标识符有效地检索最后一行?postgresql:为每个唯一标识符提取最后一行,在Postgresql中,您可能需要遇到与在数据库中的每个不同标识相关的信息中提取信息的情况。考虑以下数据:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在数据集中的每个唯一ID中检索最后一行的信息,您可以在操作员上使用Postgres的有效效率: ...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 JavaScript计算两个日期之间天数的方法How to Calculate the Difference Between Dates in JavascriptAs you attempt to determine the difference between two dates in Javascript, consider this s...编程 发布于2025-06-25
JavaScript计算两个日期之间天数的方法How to Calculate the Difference Between Dates in JavascriptAs you attempt to determine the difference between two dates in Javascript, consider this s...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 表单刷新后如何防止重复提交?在Web开发中预防重复提交 在表格提交后刷新页面时,遇到重复提交的问题是常见的。要解决这个问题,请考虑以下方法: 想象一下具有这样的代码段,看起来像这样的代码段:)){ //数据库操作... 回声“操作完成”; 死(); } ?> ...编程 发布于2025-06-25
表单刷新后如何防止重复提交?在Web开发中预防重复提交 在表格提交后刷新页面时,遇到重复提交的问题是常见的。要解决这个问题,请考虑以下方法: 想象一下具有这样的代码段,看起来像这样的代码段:)){ //数据库操作... 回声“操作完成”; 死(); } ?> ...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 解决Spring Security 4.1及以上版本CORS问题指南弹簧安全性cors filter:故障排除常见问题 在将Spring Security集成到现有项目中时,您可能会遇到与CORS相关的错误,如果像“访问Control-allo-allow-Origin”之类的标头,则无法设置在响应中。为了解决此问题,您可以实现自定义过滤器,例如代码段中的MyFi...编程 发布于2025-06-25
解决Spring Security 4.1及以上版本CORS问题指南弹簧安全性cors filter:故障排除常见问题 在将Spring Security集成到现有项目中时,您可能会遇到与CORS相关的错误,如果像“访问Control-allo-allow-Origin”之类的标头,则无法设置在响应中。为了解决此问题,您可以实现自定义过滤器,例如代码段中的MyFi...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 将图片浮动到底部右侧并环绕文字的技巧在Web设计中围绕在Web设计中,有时可以将图像浮动到页面右下角,从而使文本围绕它缠绕。这可以在有效地展示图像的同时创建一个吸引人的视觉效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮点:对; ...编程 发布于2025-06-25
将图片浮动到底部右侧并环绕文字的技巧在Web设计中围绕在Web设计中,有时可以将图像浮动到页面右下角,从而使文本围绕它缠绕。这可以在有效地展示图像的同时创建一个吸引人的视觉效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮点:对; ...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 如何限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围?在交互式接口中实现垂直滚动元素的CSS高度限制问题:考虑一个布局,其中我们具有与用户垂直滚动一起移动的可滚动地图div,同时与固定的固定sidebar保持一致。但是,地图的滚动无限期扩展,超过了视口的高度,阻止用户访问页面页脚。$("#map").css({ marginT...编程 发布于2025-06-25
如何限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围?在交互式接口中实现垂直滚动元素的CSS高度限制问题:考虑一个布局,其中我们具有与用户垂直滚动一起移动的可滚动地图div,同时与固定的固定sidebar保持一致。但是,地图的滚动无限期扩展,超过了视口的高度,阻止用户访问页面页脚。$("#map").css({ marginT...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 在C#中如何高效重复字符串字符用于缩进?在基于项目的深度下固定字符串时,重复一个字符串以进行凹痕,很方便有效地有一种有效的方法来返回字符串重复指定的次数的字符串。使用指定的次数。 constructor 这将返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.Wr...编程 发布于2025-06-25
在C#中如何高效重复字符串字符用于缩进?在基于项目的深度下固定字符串时,重复一个字符串以进行凹痕,很方便有效地有一种有效的方法来返回字符串重复指定的次数的字符串。使用指定的次数。 constructor 这将返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.Wr...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-06-25
如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 如何有效地选择熊猫数据框中的列?在处理数据操作任务时,在Pandas DataFrames 中选择列时,选择特定列的必要条件是必要的。在Pandas中,选择列的各种选项。选项1:使用列名 如果已知列索引,请使用ILOC函数选择它们。请注意,python索引基于零。 df1 = df.iloc [:,0:2]#使用索引0和1 的 ...编程 发布于2025-06-25
如何有效地选择熊猫数据框中的列?在处理数据操作任务时,在Pandas DataFrames 中选择列时,选择特定列的必要条件是必要的。在Pandas中,选择列的各种选项。选项1:使用列名 如果已知列索引,请使用ILOC函数选择它们。请注意,python索引基于零。 df1 = df.iloc [:,0:2]#使用索引0和1 的 ...编程 发布于2025-06-25 -
 Spark DataFrame添加常量列的妙招在Spark Dataframe ,将常数列添加到Spark DataFrame,该列具有适用于所有行的任意值的Spark DataFrame,可以通过多种方式实现。使用文字值(SPARK 1.3)在尝试提供直接值时,用于此问题时,旨在为此目的的column方法可能会导致错误。 df.withCo...编程 发布于2025-06-25
Spark DataFrame添加常量列的妙招在Spark Dataframe ,将常数列添加到Spark DataFrame,该列具有适用于所有行的任意值的Spark DataFrame,可以通过多种方式实现。使用文字值(SPARK 1.3)在尝试提供直接值时,用于此问题时,旨在为此目的的column方法可能会导致错误。 df.withCo...编程 发布于2025-06-25
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























