加权图类
The WeightedGraph class extends AbstractGraph.
The preceding chapter designed the Graph interface, the AbstractGraph class, and the UnweightedGraph class for modeling graphs. Following this pattern, we design WeightedGraph as a subclass of AbstractGraph, as shown in Figure below.
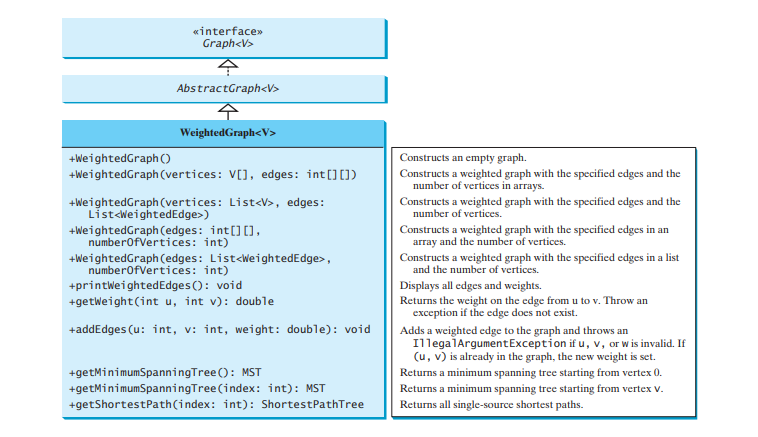
WeightedGraph simply extends AbstractGraph with five constructors for creating concrete WeightedGraph instances. WeightedGraph inherits all methods from AbstractGraph, overrides the clear and addVertex methods, implements a new addEdge method for adding a weighted edge, and also introduces new methods for obtaining minimum spanning trees and for finding all single-source shortest paths. Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths will be introduced in Sections Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths, respectively.
The code below implements WeightedGraph. Edge adjacency lists (lines 38–63) are used internally to store adjacent edges for a vertex. When a WeightedGraph is constructed, its edge adjacency lists are created (lines 47 and 57). The methods getMinimumSpanningTree() (lines 99–138) and getShortestPath() (lines 156–197) will be introduced in upcoming sections.
package demo; import java.util.*; public class WeightedGraphextends AbstractGraph { /** Construct an empty */ public WeightedGraph() {} /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edged in arrays */ public WeightedGraph(V[] vertices, int[][] edges) { createWeightedGraph(java.util.Arrays.asList(vertices), edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edges in list */ public WeightedGraph(int[][] edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices 0, 1, and edge array */ public WeightedGraph(List edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, int[][] edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (WeightedEdge edge: edges) { neighbors.get(edge.u).add(edge); // Add an edge into the list } } /** Return the weight on the edge (u, v) */ public double getWeight(int u, int v) throws Exception { for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(u)) { if (edge.v == v) { return ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight; } } throw new Exception("Edge does not exit"); } /** Display edges with weights */ public void printWeightedEdges() { for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while return new MST(startingVertex, parent, T, totalWeight); } /** MST is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class MST extends Tree { private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree public MST(int root, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double totalWeight) { super(root, parent, searchOrder); this.totalWeight = totalWeight; } public double getTotalWeight() { return totalWeight; } } /** Find single source shortest paths */ public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) { // cost[v] stores the cost of the path from v to the source double[] cost = new double[getSize()]; for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while // Create a ShortestPathTree return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex, parent, T, cost); } /** ShortestPathTree is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree { private double[] cost; // cost[v] is the cost from v to source /** Construct a path */ public ShortestPathTree(int source, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double[] cost) { super(source, parent, searchOrder); this.cost = cost; } /** Return the cost for a path from the root to vertex v */ public double getCost(int v) { return cost[v]; } /** Print paths from all vertices to the source */ public void printAllPaths() { System.out.println("All shortest paths from " vertices.get(getRoot()) " are:"); for (int i = 0; i The WeightedGraph class extends the AbstractGraph class (line 3). The properties vertices and neighbors in AbstractGraph are inherited in WeightedGraph.neighbors is a list. Each element is the list is another list that contains edges. For unweighted graph, each edge is an instance of AbstractGraph.Edge. For a weighted graph, each edge is an instance of WeightedEdge. WeightedEdge is a subtype of Edge. So you can add a weighted edge into neighbors.get(i) for a weighted graph (line 47).
The code below gives a test program that creates a graph for the one in Figure below and another graph for the one in Figure below a.
package demo; public class TestWeightedGraph { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"}; int[][] edges = { {0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097}, {1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267}, {2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435}, {3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003}, {4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496}, {5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787}, {6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214}, {7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888}, {8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810}, {9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187}, {10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239}, {11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239} }; WeightedGraphgraph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges); System.out.println("The number of vertices in graph1: " graph1.getSize()); System.out.println("The vertex with index 1 is " graph1.getVertex(1)); System.out.println("The index for Miami is " graph1.getIndex("Miami")); System.out.println("The edges for graph1:"); graph1.printWeightedEdges(); edges = new int[][] { {0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8}, {1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6} }; WeightedGraph graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5); System.out.println("\nThe edges for graph2:"); graph2.printWeightedEdges(); } } The number of vertices in graph1: 12
The vertex with index 1 is San Francisco
The index for Miami is 9
The edges for graph1:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 807) (0, 3, 1331) (0, 5, 2097)
Vertex 1: (1, 2, 381) (1, 0, 807) (1, 3, 1267)
Vertex 2: (2, 1, 381) (2, 3, 1015) (2, 4, 1663) (2, 10, 1435)
Vertex 3: (3, 4, 599) (3, 5, 1003) (3, 1, 1267)
(3, 0, 1331) (3, 2, 1015)
Vertex 4: (4, 10, 496) (4, 8, 864) (4, 5, 533) (4, 2, 1663)
(4, 7, 1260) (4, 3, 599)
Vertex 5: (5, 4, 533) (5, 7, 787) (5, 3, 1003)
(5, 0, 2097) (5, 6, 983)
Vertex 6: (6, 7, 214) (6, 5, 983)
Vertex 7: (7, 6, 214) (7, 8, 888) (7, 5, 787) (7, 4, 1260)
Vertex 8: (8, 9, 661) (8, 10, 781) (8, 4, 864)
(8, 7, 888) (8, 11, 810)
Vertex 9: (9, 8, 661) (9, 11, 1187)
Vertex 10: (10, 11, 239) (10, 4, 496) (10, 8, 781) (10, 2, 1435)
Vertex 11: (11, 10, 239) (11, 9, 1187) (11, 8, 810)The edges for graph2:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 2) (0, 3, 8)
Vertex 1: (1, 0, 2) (1, 2, 7) (1, 3, 3)
Vertex 2: (2, 3, 4) (2, 1, 7) (2, 4, 5)
Vertex 3: (3, 1, 3) (3, 4, 6) (3, 2, 4) (3, 0, 8)
Vertex 4: (4, 2, 5) (4, 3, 6)The program creates graph1 for the graph in Figure above in lines 3–27. The vertices for graph1 are defined in lines 3–5. The edges for graph1 are defined in lines 7–24. The edges are represented using a two-dimensional array. For each row i in the array, edges[i][0] and edges[i][1] indicate that there is an edge from vertex edges[i][0] to vertex edges[i][1] and the weight for the edge is edges[i][2]. For example, {0, 1, 807} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[0][0]) to vertex 1 (edges[0][1]) with weight 807 (edges[0][2]). {0, 5, 2097} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[2][0]) to vertex 5 (edges[2][1]) with weight 2097 (edges[2][2]). Line 35 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph1 to display all edges in graph1.
The program creates the edges for graph2 for the graph in Figure above a in lines 37–44. Line 46 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph2 to display all edges in graph2.
-
 如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何将多种用户类型(学生,老师和管理员)重定向到Firebase应用中的各自活动?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何将多种用户类型(学生,老师和管理员)重定向到Firebase应用中的各自活动?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-05-17
Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 可以在纯CS中将多个粘性元素彼此堆叠在一起吗?[2这里: https://webthemez.com/demo/sticky-multi-header-scroll/index.html </main> <section> { display:grid; grid-template-...编程 发布于2025-05-17
可以在纯CS中将多个粘性元素彼此堆叠在一起吗?[2这里: https://webthemez.com/demo/sticky-multi-header-scroll/index.html </main> <section> { display:grid; grid-template-...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 查找当前执行JavaScript的脚本元素方法如何引用当前执行脚本的脚本元素在某些方案中理解问题在某些方案中,开发人员可能需要将其他脚本动态加载其他脚本。但是,如果Head Element尚未完全渲染,则使用document.getElementsbytagname('head')[0] .appendChild(v)的常规方...编程 发布于2025-05-17
查找当前执行JavaScript的脚本元素方法如何引用当前执行脚本的脚本元素在某些方案中理解问题在某些方案中,开发人员可能需要将其他脚本动态加载其他脚本。但是,如果Head Element尚未完全渲染,则使用document.getElementsbytagname('head')[0] .appendChild(v)的常规方...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何在Java的全屏独家模式下处理用户输入?Handling User Input in Full Screen Exclusive Mode in JavaIntroductionWhen running a Java application in full screen exclusive mode, the usual event ha...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何在Java的全屏独家模式下处理用户输入?Handling User Input in Full Screen Exclusive Mode in JavaIntroductionWhen running a Java application in full screen exclusive mode, the usual event ha...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?在尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键时,如何使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;不工作。正确的方法采用方括号: jsobj ['key''i] ='example'1; 在JavaScript中,数组是一...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?在尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键时,如何使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;不工作。正确的方法采用方括号: jsobj ['key''i] ='example'1; 在JavaScript中,数组是一...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 解决MySQL插入Emoji时出现的\\"字符串值错误\\"异常Resolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...编程 发布于2025-05-17
解决MySQL插入Emoji时出现的\\"字符串值错误\\"异常Resolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何使用PHP将斑点(图像)正确插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call ...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何使用PHP将斑点(图像)正确插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call ...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-05-17
MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 Python中嵌套函数与闭包的区别是什么嵌套函数与python 在python中的嵌套函数不被考虑闭合,因为它们不符合以下要求:不访问局部范围scliables to incling scliables在封装范围外执行范围的局部范围。 make_printer(msg): DEF打印机(): 打印(味精) ...编程 发布于2025-05-17
Python中嵌套函数与闭包的区别是什么嵌套函数与python 在python中的嵌套函数不被考虑闭合,因为它们不符合以下要求:不访问局部范围scliables to incling scliables在封装范围外执行范围的局部范围。 make_printer(msg): DEF打印机(): 打印(味精) ...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何将MySQL数据库添加到Visual Studio 2012中的数据源对话框中?在Visual Studio 2012 尽管已安装了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但无法将MySQL数据库添加到实体框架的“ DataSource对话框”中。为了解决这一问题,至关重要的是要了解MySQL连接器v.6.5.5及以后的6.6.x版本将提供MySQL的官方Visual...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何将MySQL数据库添加到Visual Studio 2012中的数据源对话框中?在Visual Studio 2012 尽管已安装了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但无法将MySQL数据库添加到实体框架的“ DataSource对话框”中。为了解决这一问题,至关重要的是要了解MySQL连接器v.6.5.5及以后的6.6.x版本将提供MySQL的官方Visual...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 如何在无序集合中为元组实现通用哈希功能?在未订购的集合中的元素要纠正此问题,一种方法是手动为特定元组类型定义哈希函数,例如: template template template 。 struct std :: hash { size_t operator()(std :: tuple const&tuple)const {...编程 发布于2025-05-17
如何在无序集合中为元组实现通用哈希功能?在未订购的集合中的元素要纠正此问题,一种方法是手动为特定元组类型定义哈希函数,例如: template template template 。 struct std :: hash { size_t operator()(std :: tuple const&tuple)const {...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 在Python中如何创建动态变量?在Python 中,动态创建变量的功能可以是一种强大的工具,尤其是在使用复杂的数据结构或算法时,Dynamic Variable Creation的动态变量创建。 Python提供了几种创造性的方法来实现这一目标。利用dictionaries 一种有效的方法是利用字典。字典允许您动态创建密钥并分...编程 发布于2025-05-17
在Python中如何创建动态变量?在Python 中,动态创建变量的功能可以是一种强大的工具,尤其是在使用复杂的数据结构或算法时,Dynamic Variable Creation的动态变量创建。 Python提供了几种创造性的方法来实现这一目标。利用dictionaries 一种有效的方法是利用字典。字典允许您动态创建密钥并分...编程 发布于2025-05-17 -
 在C#中如何高效重复字符串字符用于缩进?在基于项目的深度下固定字符串时,重复一个字符串以进行凹痕,很方便有效地有一种有效的方法来返回字符串重复指定的次数的字符串。使用指定的次数。 constructor 这将返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.Wr...编程 发布于2025-05-17
在C#中如何高效重复字符串字符用于缩进?在基于项目的深度下固定字符串时,重复一个字符串以进行凹痕,很方便有效地有一种有效的方法来返回字符串重复指定的次数的字符串。使用指定的次数。 constructor 这将返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.Wr...编程 发布于2025-05-17
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning



























