反应虚拟 DOM
Introduction
Hi, Gleb Kotovsky is here!
Today I wanna talk about Virtual DOM, specifically - React Virtual DOM
So, the virtual DOM (Virtual Document Object Model) is a cool programming idea that keeps a "virtual" version of a user interface in memory. This version syncs up with the browser's DOM (Document Object Model) using a library.
You’ll find the virtual DOM is a big part of many JavaScript front-end frameworks, and it’s one of the reasons they’re so efficient. In this article, we're going to dive into how the virtual DOM works in React and why it’s important for the library.
What is the DOM?
When a webpage loads in a browser, it typically receives an HTML document from the server. The browser then builds a logical, tree-like structure from this HTML to render the requested page for the user. This structure is known as the DOM.
The Document Object Model (DOM) represents a logical tree that describes a document. Each branch of the tree ends in a node , which contains an object . Because the browser parses the document into this tree structure, there is a need for methods that allow for programmatic access to the tree, enabling modifications to the document's structure, style, or content. This necessity led to the development of the DOM API, which offers these methods for manipulating the nodes representing the elements in the tree.
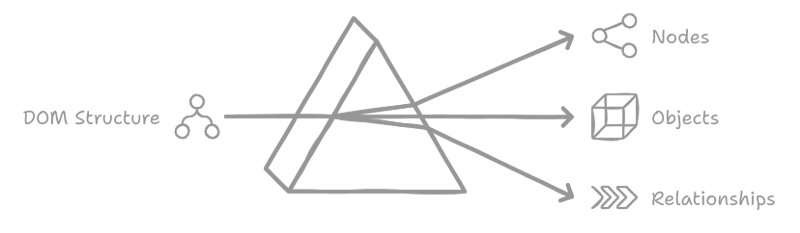
React's Virtual DOM Implementation
To optimize re-rendering in websites and applications, many JavaScript frameworks offer different strategies. However, React employs the concept of the virtual DOM.
The virtual DOM in React represents the user interface as a "virtual" tree structure, where each element is a node containing an object. This representation is maintained in memory and synchronized with the browser's DOM through React's React DOM library.
When React and many other famous frameworks uses Virtual DOM, Svelte meanwhile has no Virtual DOM. Svelte works directly with the DOM in the browser and modifies it as needed.
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Count: {count}
);
}
In this example:
- The component renders a counter and a button.
- When the button is clicked, the state is updated, prompting React to create a new Virtual DOM tree.
- The diffing algorithm checks what has changed (only the count) and updates the real DOM accordingly.
After the component is first rendered and the state is count: 0, the actual DOM will look like this:
Counter
Count: 0
How the Virtual DOM Works:
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component, starting with the component definition:
1. Component Definition
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Counter
Count: {count}
);
}
2. Initial Render Process
2.1 Component Initialization
When the component is first rendered, React calls the Counter function.
2.2 State Initialization
useState(0) initializes the component's state to 0.
2.3 Creating the Virtual DOM
React generates a Virtual DOM tree using the component's returned JSX structure. This tree is a lightweight representation of the UI.
For the initial render, the Virtual DOM might look like this:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 0" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
2.4 Updating the Real DOM
React then takes this Virtual DOM and calculates what changes need to be made to the actual DOM. In this case, it creates the following HTML:
Counter
Count: 0
3. User Interaction
When a user clicks the "Increment" button, the following steps occur:
3.1 Event Handling
The button's onClick event triggers the increment function, calling setCount(count 1).
3.2 State Update
The component's state is updated, which causes React to know that it needs to re-render the component with the new state.
4. Re-render Process
4.1 Component Re-invocation
React calls the Counter function again due to the state change.
4.2 New Virtual DOM Creation
A new Virtual DOM tree is created reflecting the updated state:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 1" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
4.3 Diffing the Virtual DOM
React compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous Virtual DOM. It identifies what has changed—in this case, the text in the
tag has changed from "Count: 0" to "Count: 1".
4.4 Reconciliation
Only the parts of the real DOM that have changed are updated. In this case, React updates the real DOM to reflect the new count:
Counter
Count: 1
5. Performance Optimization
5.1 Batching Updates
If multiple state updates occur in rapid succession (e.g., multiple button clicks), React may batch these updates together for efficiency, minimizing the number of re-renders and DOM updates.
Common Problems with React Virtual DOM and How to Avoid Them
-
Performance Bottlenecks
- Issue: Excessive re-renders can occur even with the Virtual DOM.
- Solution: Use React.memo to memoize functional components.
const MyComponent = React.memo(({ value }) => {
console.log('Rendered: ', value);
return {value};
});
Legacy: Use shouldComponentUpdate in class components:
class MyClassComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps) {
return nextProps.value !== this.props.value;
}
render() {
return {this.props.value};
}
}
-
Inefficient Key Management
- Issue: Improper handling of keys in lists can lead to bugs.
- Solution: Use unique and stable keys, not array indices.
const items = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry'];
return (
-
{items.map(item => (
- {item} // Prefer unique values as keys ))}
-
Overusing State and Updates
- Issue: Too many state updates lead to performance issues.
- Solution: Combine related states
const [state, setState] = useState({
name: '',
age: 0,
});
const updateAge = (newAge) => {
setState(prevState => ({ ...prevState, age: newAge }));
};
-
Using Inline Functions
- Issue: Inline functions create new instances on every render.
- Solution: Use useCallback to memoize functions.
const increment = useCallback(() => {
setCount(c => c 1);
}, []); // Only recreate the function if dependencies change
-
Deep Component Trees
- Issue: Deeply nested components trigger multiple re-renders.
- Solution: Use context.
const CountContext = React.createContext();
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
);
};
const ChildComponent = () => {
const { count, setCount } = useContext(CountContext);
return setCount(count 1)}>Count: {count};
};
-
Excessive Re-renders Due to Parent Component Updates
- Issue: Child components re-render when parents update.
- Solution: Memoize child components.
const ChildComponent = React.memo(({ count }) => {
return Count: {count};
});
-
Inefficient Rendering of Expensive Components
- Issue: Expensive components can slow down the app.
- Solution: Use React.lazy and React.Suspense.
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
const App = () => (
Loading...}>
);
-
Managing Side Effects
- Issue: Side effects can cause bugs if not managed properly.
- Solution: Use useEffect with proper dependencies.
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Time elapsed');
}, 1000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer); // Cleanup on unmount or if dependencies change
}, [dependencies]); // Replace with actual dependency
-
Confusion Between State and Props
- Issue: Misunderstanding when to use state vs. props.
- Solution: Use props for externally managed data and state for local data.
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('John');
return {name}
);
-
Neglecting Accessibility
- Issue: Accessibility concerns can be ignored.
- Solution: Use semantic HTML and accessibility tools.
const AccessibleButton = () => ( );
Conclusion
To wrap things up, React’s Virtual DOM is a fantastic feature that really boosts the performance of your web applications. By creating a lightweight version of the actual DOM, React can make updates more efficiently, avoiding the slowdowns that come with direct DOM manipulation.
That said, it’s important to watch out for common issues like excessive re-renders, poor key management in lists, and mixing up state and props. By keeping some best practices in mind—like using memoization, deploying context for handling state, and managing side effects wisely—you can get the most out of React and keep your apps running smoothly.
Happy hacking!
Resources
1) https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/reactjs-virtual-dom/
2) https://svelte.dev/blog/virtual-dom-is-pure-overhead
3) https://refine.dev/blog/react-virtual-dom/#introduction
-
 PHP与C++函数重载处理的区别作为经验丰富的C开发人员脱离谜题,您可能会遇到功能超载的概念。这个概念虽然在C中普遍,但在PHP中构成了独特的挑战。让我们深入研究PHP功能过载的复杂性,并探索其提供的可能性。在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函数超载的概念(如C等语言)不存在。函数签名仅由其名称定义,而与他们的参数列表无关。...编程 发布于2025-05-02
PHP与C++函数重载处理的区别作为经验丰富的C开发人员脱离谜题,您可能会遇到功能超载的概念。这个概念虽然在C中普遍,但在PHP中构成了独特的挑战。让我们深入研究PHP功能过载的复杂性,并探索其提供的可能性。在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函数超载的概念(如C等语言)不存在。函数签名仅由其名称定义,而与他们的参数列表无关。...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 Async Void vs. Async Task在ASP.NET中:为什么Async Void方法有时会抛出异常?在ASP.NET async void void async void void void void void void void的设计无需返回asynchroncon而无需返回任务对象。他们在执行过程中增加未偿还操作的计数,并在完成后减少。在某些情况下,这种行为可能是有益的,例如未期望或明确...编程 发布于2025-05-02
Async Void vs. Async Task在ASP.NET中:为什么Async Void方法有时会抛出异常?在ASP.NET async void void async void void void void void void void的设计无需返回asynchroncon而无需返回任务对象。他们在执行过程中增加未偿还操作的计数,并在完成后减少。在某些情况下,这种行为可能是有益的,例如未期望或明确...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何从Python中的字符串中删除表情符号:固定常见错误的初学者指南?从python import codecs import codecs import codecs 导入 text = codecs.decode('这狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#带有...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何从Python中的字符串中删除表情符号:固定常见错误的初学者指南?从python import codecs import codecs import codecs 导入 text = codecs.decode('这狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#带有...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 左连接为何在右表WHERE子句过滤时像内连接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小时在数据库Wizard的领域中变成内在的加入很有趣,当将c.foobar条件放置在上面的Where子句中时,据说左联接似乎会转换为内部连接。仅当满足A.Foo和C.Foobar标准时,才会返回结果。为什么要变形?关键在于其中的子句。当左联接的右侧值...编程 发布于2025-05-02
左连接为何在右表WHERE子句过滤时像内连接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小时在数据库Wizard的领域中变成内在的加入很有趣,当将c.foobar条件放置在上面的Where子句中时,据说左联接似乎会转换为内部连接。仅当满足A.Foo和C.Foobar标准时,才会返回结果。为什么要变形?关键在于其中的子句。当左联接的右侧值...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何从2D数组中提取元素?使用另一数组的索引Using NumPy Array as Indices for the 2nd Dimension of Another ArrayTo extract specific elements from a 2D array based on indices provided by a second ...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何从2D数组中提取元素?使用另一数组的索引Using NumPy Array as Indices for the 2nd Dimension of Another ArrayTo extract specific elements from a 2D array based on indices provided by a second ...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 哪种在JavaScript中声明多个变量的方法更可维护?在JavaScript中声明多个变量:探索两个方法在JavaScript中,开发人员经常遇到需要声明多个变量的需要。对此的两种常见方法是:在单独的行上声明每个变量: 当涉及性能时,这两种方法本质上都是等效的。但是,可维护性可能会有所不同。 第一个方法被认为更易于维护。每个声明都是其自己的语句,使其...编程 发布于2025-05-02
哪种在JavaScript中声明多个变量的方法更可维护?在JavaScript中声明多个变量:探索两个方法在JavaScript中,开发人员经常遇到需要声明多个变量的需要。对此的两种常见方法是:在单独的行上声明每个变量: 当涉及性能时,这两种方法本质上都是等效的。但是,可维护性可能会有所不同。 第一个方法被认为更易于维护。每个声明都是其自己的语句,使其...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 PHP阵列键值异常:了解07和08的好奇情况PHP数组键值问题,使用07&08 在给定数月的数组中,键值07和08呈现令人困惑的行为时,就会出现一个不寻常的问题。运行print_r($月份)返回意外结果:键“ 07”丢失,而键“ 08”分配给了9月的值。此问题源于PHP对领先零的解释。当一个数字带有0(例如07或08)的前缀时,PHP将...编程 发布于2025-05-02
PHP阵列键值异常:了解07和08的好奇情况PHP数组键值问题,使用07&08 在给定数月的数组中,键值07和08呈现令人困惑的行为时,就会出现一个不寻常的问题。运行print_r($月份)返回意外结果:键“ 07”丢失,而键“ 08”分配给了9月的值。此问题源于PHP对领先零的解释。当一个数字带有0(例如07或08)的前缀时,PHP将...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 FastAPI自定义404页面创建指南response = await call_next(request) if response.status_code == 404: return RedirectResponse("https://fastapi.tiangolo.com") else: ...编程 发布于2025-05-02
FastAPI自定义404页面创建指南response = await call_next(request) if response.status_code == 404: return RedirectResponse("https://fastapi.tiangolo.com") else: ...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 解决MySQL插入Emoji时出现的\\"字符串值错误\\"异常Resolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...编程 发布于2025-05-02
解决MySQL插入Emoji时出现的\\"字符串值错误\\"异常Resolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 在程序退出之前,我需要在C ++中明确删除堆的堆分配吗?在C中的显式删除 在C中的动态内存分配时,开发人员通常会想知道是否有必要在heap-procal extrable exit exit上进行手动调用“ delete”操作员,但开发人员通常会想知道是否需要手动调用“ delete”操作员。本文深入研究了这个主题。 在C主函数中,使用了动态分配变量(H...编程 发布于2025-05-02
在程序退出之前,我需要在C ++中明确删除堆的堆分配吗?在C中的显式删除 在C中的动态内存分配时,开发人员通常会想知道是否有必要在heap-procal extrable exit exit上进行手动调用“ delete”操作员,但开发人员通常会想知道是否需要手动调用“ delete”操作员。本文深入研究了这个主题。 在C主函数中,使用了动态分配变量(H...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何克服PHP的功能重新定义限制?克服PHP的函数重新定义限制在PHP中,多次定义一个相同名称的函数是一个no-no。尝试这样做,如提供的代码段所示,将导致可怕的“不能重新列出”错误。 但是,PHP工具腰带中有一个隐藏的宝石:runkit扩展。它使您能够灵活地重新定义函数。 runkit_function_renction_re...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何克服PHP的功能重新定义限制?克服PHP的函数重新定义限制在PHP中,多次定义一个相同名称的函数是一个no-no。尝试这样做,如提供的代码段所示,将导致可怕的“不能重新列出”错误。 但是,PHP工具腰带中有一个隐藏的宝石:runkit扩展。它使您能够灵活地重新定义函数。 runkit_function_renction_re...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 在GO中构造SQL查询时,如何安全地加入文本和值?在go中构造文本sql查询时,在go sql queries 中,在使用conting and contement和contement consem per时,尤其是在使用integer per当per当per时,per per per当per. [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&默元组方法在...编程 发布于2025-05-02
在GO中构造SQL查询时,如何安全地加入文本和值?在go中构造文本sql查询时,在go sql queries 中,在使用conting and contement和contement consem per时,尤其是在使用integer per当per当per时,per per per当per. [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&默元组方法在...编程 发布于2025-05-02 -
 如何在Java的全屏独家模式下处理用户输入?在Java 中,以全屏幕独立模式运行Java应用程序时,通常无法按期望的工作可能无法使用JAVA应用程序时,将用户输入在Java ProblemPassive rendering mode allows the use of KeyListener and ActionListener inter...编程 发布于2025-05-02
如何在Java的全屏独家模式下处理用户输入?在Java 中,以全屏幕独立模式运行Java应用程序时,通常无法按期望的工作可能无法使用JAVA应用程序时,将用户输入在Java ProblemPassive rendering mode allows the use of KeyListener and ActionListener inter...编程 发布于2025-05-02
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























