Mysql資料庫索引初學者詳解
Core Concepts
- Primary Key Index / Secondary Index
- Clustered Index / Non-Clustered Index
- Table Lookup / Index Covering
- Index Pushdown
- Composite Index / Leftmost Prefix Matching
- Prefix Index
- Explain
1. [Index Definition]
1. Index Definition
Besides the data itself, the database system also maintains data structures that satisfy specific search algorithms. These structures reference (point to) the data in a certain way, allowing advanced search algorithms to be implemented on them. These data structures are indexes.
2. Data Structures of Indexes
- B-tree / B tree (MySQL's InnoDB engine uses B tree as the default index structure)
- HASH table
- Sorted array
3. Why Choose B Tree Over B Tree
- B-tree structure: Records are stored in the tree nodes.
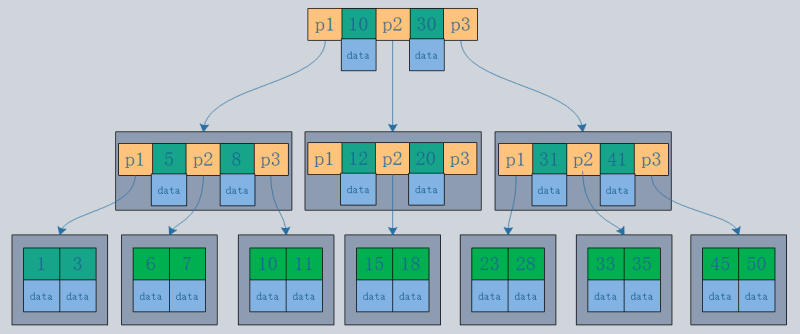
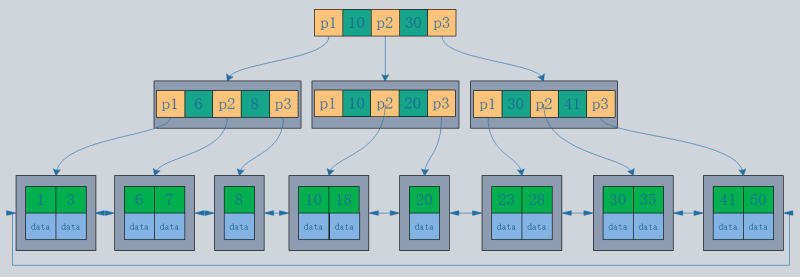
- B tree structure: Records are stored only in the leaf nodes of the tree.
- Assuming a data size of 1KB and an index size of 16B, with the database using disk data pages, and a default disk page size of 16K, the same three I/O operations will yield:
B-tree can fetch 16*16*16=4096 records.
B tree can fetch 1000*1000*1000=1 billion records.
2. [Index Types]
1. Primary Key Index and Secondary Index
- Primary Key Index: The leaf nodes of the index are data rows.
- Secondary Index: The leaf nodes of the index are KEY fields plus primary key index. Therefore, when querying through a secondary index, it first finds the primary key value, and then InnoDB finds the corresponding data block through the primary key index.
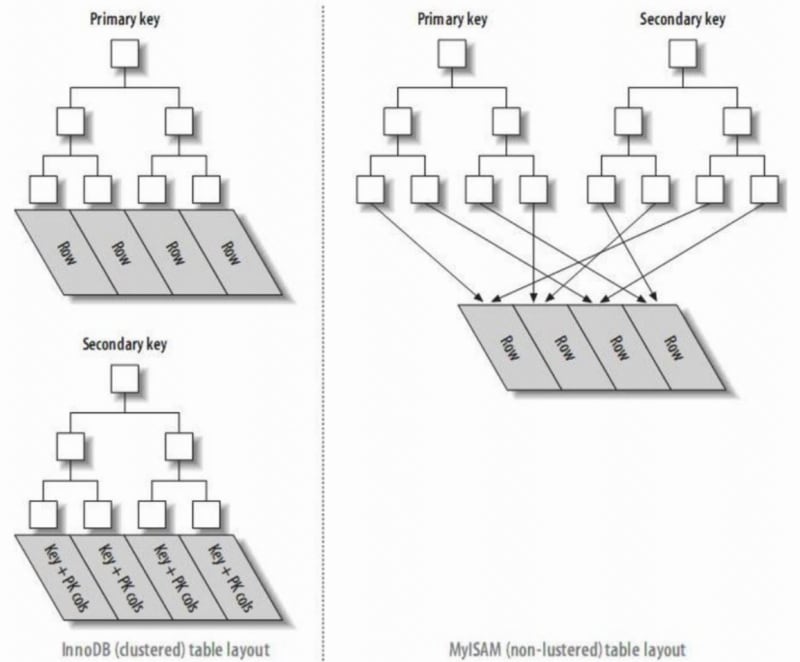
- In InnoDB, the primary index file directly stores the data row, called clustered index, while secondary indexes point to the primary key reference.
- In MyISAM, both primary and secondary indexes point to physical rows (disk positions).
2. Clustered Index and Non-Clustered Index
- A clustered index reorganizes the actual data on the disk to be sorted by one or more specified column values. The characteristic is that the storage order of the data and the index order are consistent. Generally, the primary key will default to creating a clustered index, and a table only allows one clustered index (reason: data can only be stored in one order). As shown in the image, InnoDB's primary and secondary indexes are clustered indexes.
- Compared to the leaf nodes of a clustered index being data records, the leaf nodes of a non-clustered index are pointers to the data records. The biggest difference is that the order of data records does not match the index order.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Clustered Index
- Advantage: When querying entries by primary key, it does not need to perform a table lookup (data is under the primary key node).
- Disadvantage: Frequent page splits can occur with irregular data insertion.
3. [Extended Index Concepts]
1. Table Lookup
The concept of table lookup involves the difference between primary key index and non-primary key index queries.
- If the query is select * from T where ID=500, a primary key query only needs to search the ID tree.
- If the query is select * from T where k=5, a non-primary key index query needs to first search the k index tree to get the ID value of 500, then search the ID index tree again.
- The process of moving from the non-primary key index back to the primary key index is called table lookup.
Queries based on non-primary key indexes require scanning an additional index tree. Therefore, we should try to use primary key queries in applications. From the perspective of storage space, since the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index tree store primary key values, it is advisable to keep the primary key fields as short as possible. This way, the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index tree are smaller, and the non-primary key index occupies less space. Generally, it is recommended to create an auto-increment primary key to minimize the space occupied by non-primary key indexes.
2. Index Covering
- If a WHERE clause condition is a non-primary key index, the query will first locate the primary key index through the non-primary key index (the primary key is located at the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index search tree), and then locate the query content through the primary key index. In this process, moving back to the primary key index tree is called table lookup.
- However, when our query content is the primary key value, we can directly provide the query result without table lookup. In other words, the non-primary key index has already "covered" our query requirement in this query, hence it is called a covering index.
- A covering index can directly obtain query results from the auxiliary index without table lookup to the primary index, thereby reducing the number of searches (not needing to move from the auxiliary index tree to the clustered index tree) or reducing IO operations (the auxiliary index tree can load more nodes from the disk at once), thereby improving performance.
3. Composite Index
A composite index refers to indexing multiple columns of a table.
Scenario 1:
A composite index (a, b) is sorted by a, b (first sorted by a, if a is the same then sorted by b). Therefore, the following statements can directly use the composite index to get results (in fact, it uses the leftmost prefix principle):
- select … from xxx where a=xxx;
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by b;
The following statements cannot use composite queries:
- select … from xxx where b=xxx;
Scenario 2:
For a composite index (a, b, c), the following statements can directly get results through the composite index:
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by b;
- select … from xxx where a=xxx and b=xxx order by c;
The following statements cannot use the composite index and require a filesort operation:
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by c;
Summary:
Using the composite index (a, b, c) as an example, creating such an index is equivalent to creating indexes a, ab, and abc. Having one index replace three indexes is certainly beneficial, as each additional index increases the overhead of write operations and disk space usage.
4. Leftmost Prefix Principle
- From the above composite index example, we can understand the leftmost prefix principle.
- Not just the full definition of the index, as long as it meets the leftmost prefix, it can be used to speed up retrieval. This leftmost prefix can be the leftmost N fields of the composite index or the leftmost M characters of the string index. Use the "leftmost prefix" principle of the index to locate records and avoid redundant index definitions.
- Therefore, based on the leftmost prefix principle, it is crucial to consider the field order within the index when defining composite indexes! The evaluation criterion is the reusability of the index. For example, when there is already an index on (a, b), there is generally no need to create a separate index on a.
5. Index Pushdown
MySQL 5.6 introduced the index pushdown optimization, which can filter out records that do not meet the conditions based on the fields included in the index during index traversal, reducing the number of table lookups.
- Create table
CREATE TABLE `test` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Auto-increment primary key', `age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 NOT NULL DEFAULT '', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_name_age` (`name`,`age`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
- SELECT * from user where name like 'Chen%' Leftmost prefix principle, hitting idx_name_age index
-
SELECT * from user where name like 'Chen%' and age=20
- Before version 5.6, it would first match 2 records based on the name index (ignoring the age=20 condition at this point), find the corresponding 2 IDs, perform table lookups, and then filter based on age=20.
- After version 5.6, index pushdown is introduced. After matching 2 records based on name, it will not ignore the age=20 condition before performing table lookups, filtering based on age before table lookup. This index pushdown can reduce the number of table lookups and improve query performance.
6. Prefix Index
When an index is a long character sequence, it can take up a lot of memory and be slow. In this case, prefix indexes can be used. Instead of indexing the entire value, we index the first few characters to save space and achieve good performance. Prefix index uses the first few letters of the index. However, to reduce the index duplication rate, we must evaluate the uniqueness of the prefix index.
- First, calculate the uniqueness ratio of the current string field: select 1.0*count(distinct name)/count(*) from test
- Then, calculate the uniqueness ratio for different prefixes:
- select 1.0*count(distinct left(name,1))/count(*) from test for the first character of the name as the prefix index
- select 1.0*count(distinct left(name,2))/count(*) from test for the first two characters of the name as the prefix index
- ...
- When left(str, n) does not significantly increase, select n as the prefix index cut-off value.
- Create the index alter table test add key(name(n));
4. [Viewing Indexes]
After adding indexes, how do we view them? Or, if statements are slow to execute, how do we troubleshoot?
Explain is commonly used to check if an index is effective.
After obtaining the slow query log, observe which statements are slow. Add explain before the statement and execute it again. Explain sets a flag on the query, causing it to return information about each step in the execution plan instead of executing the statement. It returns one or more rows of information showing each part of the execution plan and the execution order.
Important fields returned by explain:
- type: Shows the search method (full table scan or index scan)
- key: The index field used, null if not used
Explain's type field:
- ALL: Full table scan
- index: Full index scan
- range: Index range scan
- ref: Non-unique index scan
- eq_ref: Unique index scan
-
 MySQL中如何高效地根據兩個條件INSERT或UPDATE行?在兩個條件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在於mysql的插入中...在重複鍵更新語法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新現有行,則此功能強大的功能可以通過插入新行來進行有效的數據操作。如果違反了唯一的密鑰約束。 實現所需的行為,該表必須具有唯一的鍵定義(在這種情況下為'名稱'...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
MySQL中如何高效地根據兩個條件INSERT或UPDATE行?在兩個條件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在於mysql的插入中...在重複鍵更新語法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新現有行,則此功能強大的功能可以通過插入新行來進行有效的數據操作。如果違反了唯一的密鑰約束。 實現所需的行為,該表必須具有唯一的鍵定義(在這種情況下為'名稱'...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 為什麼我在Silverlight Linq查詢中獲得“無法找到查詢模式的實現”錯誤?查詢模式實現缺失:解決“無法找到”錯誤在銀光應用程序中,嘗試使用LINQ建立錯誤的數據庫連接的嘗試,無法找到以查詢模式的實現。 ”當省略LINQ名稱空間或查詢類型缺少IEnumerable 實現時,通常會發生此錯誤。 解決問題來驗證該類型的質量是至關重要的。在此特定實例中,tblpersoon可能...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
為什麼我在Silverlight Linq查詢中獲得“無法找到查詢模式的實現”錯誤?查詢模式實現缺失:解決“無法找到”錯誤在銀光應用程序中,嘗試使用LINQ建立錯誤的數據庫連接的嘗試,無法找到以查詢模式的實現。 ”當省略LINQ名稱空間或查詢類型缺少IEnumerable 實現時,通常會發生此錯誤。 解決問題來驗證該類型的質量是至關重要的。在此特定實例中,tblpersoon可能...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 用戶本地時間格式及時區偏移顯示指南在用戶的語言環境格式中顯示日期/時間,並使用時間偏移在向最終用戶展示日期和時間時,以其localzone and格式顯示它們至關重要。這確保了不同地理位置的清晰度和無縫用戶體驗。以下是使用JavaScript實現此目的的方法。 方法:推薦方法是處理客戶端的Javascript中的日期/時間格式化和...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
用戶本地時間格式及時區偏移顯示指南在用戶的語言環境格式中顯示日期/時間,並使用時間偏移在向最終用戶展示日期和時間時,以其localzone and格式顯示它們至關重要。這確保了不同地理位置的清晰度和無縫用戶體驗。以下是使用JavaScript實現此目的的方法。 方法:推薦方法是處理客戶端的Javascript中的日期/時間格式化和...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 Go web應用何時關閉數據庫連接?在GO Web Applications中管理數據庫連接很少,考慮以下簡化的web應用程序代碼:出現的問題:何時應在DB連接上調用Close()方法? ,該特定方案將自動關閉程序時,該程序將在EXITS EXITS EXITS出現時自動關閉。但是,其他考慮因素可能保證手動處理。 選項1:隱式關閉終...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
Go web應用何時關閉數據庫連接?在GO Web Applications中管理數據庫連接很少,考慮以下簡化的web應用程序代碼:出現的問題:何時應在DB連接上調用Close()方法? ,該特定方案將自動關閉程序時,該程序將在EXITS EXITS EXITS出現時自動關閉。但是,其他考慮因素可能保證手動處理。 選項1:隱式關閉終...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 如何在鼠標單擊時編程選擇DIV中的所有文本?在鼠標上選擇div文本單擊帶有文本內容,用戶如何使用單個鼠標單擊單擊div中的整個文本?這允許用戶輕鬆拖放所選的文本或直接複製它。 在單個鼠標上單擊的div元素中選擇文本,您可以使用以下Javascript函數: function selecttext(canduterid){ if(d...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
如何在鼠標單擊時編程選擇DIV中的所有文本?在鼠標上選擇div文本單擊帶有文本內容,用戶如何使用單個鼠標單擊單擊div中的整個文本?這允許用戶輕鬆拖放所選的文本或直接複製它。 在單個鼠標上單擊的div元素中選擇文本,您可以使用以下Javascript函數: function selecttext(canduterid){ if(d...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 在JavaScript中如何並發運行異步操作並正確處理錯誤?同意操作execution 在執行asynchronous操作時,相關的代碼段落會遇到一個問題,當執行asynchronous操作:此實現在啟動下一個操作之前依次等待每個操作的完成。要啟用並發執行,需要進行修改的方法。 第一個解決方案試圖通過獲得每個操作的承諾來解決此問題,然後單獨等待它們: c...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
在JavaScript中如何並發運行異步操作並正確處理錯誤?同意操作execution 在執行asynchronous操作時,相關的代碼段落會遇到一個問題,當執行asynchronous操作:此實現在啟動下一個操作之前依次等待每個操作的完成。要啟用並發執行,需要進行修改的方法。 第一個解決方案試圖通過獲得每個操作的承諾來解決此問題,然後單獨等待它們: c...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 如何在Java中正確顯示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的當前日期和時間?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解決方案: args)拋出異常{ 日曆cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
如何在Java中正確顯示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的當前日期和時間?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解決方案: args)拋出異常{ 日曆cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 CSS可以根據任何屬性值來定位HTML元素嗎?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何屬性值,在CSS中,可以基於特定屬性(如下所示)基於特定屬性的基於特定屬性的emants目標元素: 字體家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出現一個常見的問題:元素可以根據任何屬性值而定位嗎?本文探討了此主題。 的目標元素有任何任何屬性值,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
CSS可以根據任何屬性值來定位HTML元素嗎?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何屬性值,在CSS中,可以基於特定屬性(如下所示)基於特定屬性的基於特定屬性的emants目標元素: 字體家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出現一個常見的問題:元素可以根據任何屬性值而定位嗎?本文探討了此主題。 的目標元素有任何任何屬性值,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 如何從Python中的字符串中刪除表情符號:固定常見錯誤的初學者指南?從python import codecs import codecs import codecs 導入 text = codecs.decode('這狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#帶有...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
如何從Python中的字符串中刪除表情符號:固定常見錯誤的初學者指南?從python import codecs import codecs import codecs 導入 text = codecs.decode('這狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#帶有...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 Java中假喚醒真的會發生嗎?在Java中的浪費喚醒:真實性或神話? 在Java同步中偽裝喚醒的概念已經是討論的主題。儘管存在這種行為的潛力,但問題仍然存在:它們實際上是在實踐中發生的嗎? Linux的喚醒機制根據Wikipedia關於偽造喚醒的文章,linux實現了pthread_cond_wait()功能的Linux實現,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
Java中假喚醒真的會發生嗎?在Java中的浪費喚醒:真實性或神話? 在Java同步中偽裝喚醒的概念已經是討論的主題。儘管存在這種行為的潛力,但問題仍然存在:它們實際上是在實踐中發生的嗎? Linux的喚醒機制根據Wikipedia關於偽造喚醒的文章,linux實現了pthread_cond_wait()功能的Linux實現,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安裝mysql-python時,如何修復\“ mysql_config \”錯誤?mysql-python安裝錯誤:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由於缺少MySQL開發庫而出現此錯誤。解決此問題,建議在Ubuntu上使用該分發的存儲庫。使用以下命令安裝Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安裝python-mysqldb sudo pip in...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
在Ubuntu/linux上安裝mysql-python時,如何修復\“ mysql_config \”錯誤?mysql-python安裝錯誤:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由於缺少MySQL開發庫而出現此錯誤。解決此問題,建議在Ubuntu上使用該分發的存儲庫。使用以下命令安裝Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安裝python-mysqldb sudo pip in...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 如何將MySQL數據庫添加到Visual Studio 2012中的數據源對話框中?在Visual Studio 2012 儘管已安裝了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但無法將MySQL數據庫添加到實體框架的“ DataSource對話框”中。為了解決這一問題,至關重要的是要了解MySQL連接器v.6.5.5及以後的6.6.x版本將提供MySQL的官方Visual...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
如何將MySQL數據庫添加到Visual Studio 2012中的數據源對話框中?在Visual Studio 2012 儘管已安裝了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但無法將MySQL數據庫添加到實體框架的“ DataSource對話框”中。為了解決這一問題,至關重要的是要了解MySQL連接器v.6.5.5及以後的6.6.x版本將提供MySQL的官方Visual...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 如何使用不同數量列的聯合數據庫表?合併列數不同的表 當嘗試合併列數不同的數據庫表時,可能會遇到挑戰。一種直接的方法是在列數較少的表中,為缺失的列追加空值。 例如,考慮兩個表,表 A 和表 B,其中表 A 的列數多於表 B。為了合併這些表,同時處理表 B 中缺失的列,請按照以下步驟操作: 確定表 B 中缺失的列,並將它們添加到表的...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
如何使用不同數量列的聯合數據庫表?合併列數不同的表 當嘗試合併列數不同的數據庫表時,可能會遇到挑戰。一種直接的方法是在列數較少的表中,為缺失的列追加空值。 例如,考慮兩個表,表 A 和表 B,其中表 A 的列數多於表 B。為了合併這些表,同時處理表 B 中缺失的列,請按照以下步驟操作: 確定表 B 中缺失的列,並將它們添加到表的...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14 -
 PHP未來:適應與創新PHP的未來將通過適應新技術趨勢和引入創新特性來實現:1)適應云計算、容器化和微服務架構,支持Docker和Kubernetes;2)引入JIT編譯器和枚舉類型,提升性能和數據處理效率;3)持續優化性能和推廣最佳實踐。 引言在編程世界中,PHP一直是網頁開發的中流砥柱。作為一個從1994年就開始發展...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
PHP未來:適應與創新PHP的未來將通過適應新技術趨勢和引入創新特性來實現:1)適應云計算、容器化和微服務架構,支持Docker和Kubernetes;2)引入JIT編譯器和枚舉類型,提升性能和數據處理效率;3)持續優化性能和推廣最佳實踐。 引言在編程世界中,PHP一直是網頁開發的中流砥柱。作為一個從1994年就開始發展...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-14
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























