如何為 Laravel API 建立緩存層
Let's say you are building an API to serve some data, you discover GET responses are quite slow. You have tried optimizing your queries, indexing your database tables by frequently queried columns and you are still not getting the response times you want. The next step to take is to write a Caching layer for your API. 'Caching layer' here is just a fancy term for a middleware that stores successful responses in a fast to retrieve store. e.g. Redis, Memcached etc. then any further requests to the API checks if the data is available in the store and serves the response.
Prerequisites
- Laravel
- Redis
Before we start
I am assuming if you have gotten here, you know how to create a laravel app. You should also have either a local or cloud Redis instance to connect to. If you have docker locally, you can copy my compose file here. Also, for a guide on how to connect to the Redis cache driver read here.
Creating our Dummy Data
To help us see our caching layer is working as expected. of course we need some data let's say we have a model named Post. so I will be creating some posts, I will also add some complex filtering that could be database intensive and then we can optimize by caching.
Now let's start writing our middleware:
We create our middleware skeleton by running
php artisan make:middleware CacheLayer
Then register it in your app/Http/Kernel.php under the api middleware group like so:
protected $middlewareGroups = [
'api' => [
CacheLayer::class,
],
];
But if you are running Laravel 11. register it in your bootstrap/app.php
->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) {
$middleware->api(append: [
\App\Http\Middleware\CacheLayer::class,
]);
})
Caching Terminologies
- Cache Hit: occurs when data requested is found in the cache.
- Cache Miss: happens when the requested data is not found in the cache.
- Cache Flush: clearing out the stored data in the cache so that it can be repopulated with fresh data.
- Cache tags: This is a feature unique to Redis. cache tags are a feature used to group related items in the cache, making it easier to manage and invalidate related data simultaneously.
- Time to Live (TTL): this refers to the amount of time a cached object stays valid before it expires. One common misunderstanding is thinking that every time an object is accessed from the cache (a cache hit), its expiry time gets reset. However, this isn't true. For instance, if the TTL is set to 5 minutes, the cached object will expire after 5 minutes, no matter how many times it's accessed within that period. After the 5 minutes are up, the next request for that object will result in a new entry being created in the cache.
Computing a Unique Cache Key
So cache drivers are a key-value store. so you have a key then the value is your json. So you need a unique cache key to identify resources, a unique cache key will also help in cache invalidation i.e. removing cache items when a new resource is created/updated. My approach for cache key generation is to turn the request url, query params, and body into an object. then serialize it to string. Add this to your cache middleware:
class CacheLayer
{
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
}
private function getCacheKey(Request $request): string
{
$routeParameters = ! empty($request->route()->parameters) ? $request->route()->parameters : [auth()->user()->id];
$allParameters = array_merge($request->all(), $routeParameters);
$this->recursiveSort($allParameters);
return $request->url() . json_encode($allParameters);
}
private function recursiveSort(&$array): void
{
foreach ($array as &$value) {
if (is_array($value)) {
$this->recursiveSort($value);
}
}
ksort($array);
}
}
Let's go through the code line by line.
- First we check for the matched request parameters. we don't want to compute the same cache key for /users/1/posts and /users/2/posts.
- And if there are no matched parameters we pass in the user's id. This part is optional. If you have routes like /user that returns details for the currently authenticated user. it will be suitable to pass in the user id in the cache key. if not you can just make it an empty array([]).
- Then we get all the query parameters and merge it with the request parameters
- Then we sort the parameters, why this sorting step is very important is so we can return same data for let's say /posts?page=1&limit=20 and /posts?limit=20&page=1. so regardless of the order of the parameters we still return the same cache key.
Excluding routes
So depending on the nature of the application you are building. There will be some GET routes that you don't want to cache so for this we create a constant with the regex to match those routes. This will look like:
private const EXCLUDED_URLS = [
'~^api/v1/posts/[0-9a-zA-Z] /comments(\?.*)?$~i'
'
];
In this case, this regex will match all a post's comments.
Configuring TTL
For this, just add this entry to your config/cache.php
'ttl' => now()->addMinutes(5),
Writing our Middleware
Now we have all our preliminary steps set we can write our middleware code:
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
if ('GET' !== $method) {
return $next($request);
}
foreach (self::EXCLUDED_URLS as $pattern) {
if (preg_match($pattern, $request->getRequestUri())) {
return $next($request);
}
}
$cacheKey = $this->getCacheKey($request);
$exception = null;
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return $res;
}
);
return $exception ?? $response;
}
- First we skip caching for non-GET requests and Excluded urls.
- Then we use the cache helper, tag that cache entry by the request url.
- we use the remember method to store that cache entry. then we call the other handlers down the stack by doing $next($request). we check for exceptions. and then either return the exception or response.
Cache Invalidation
When new resources are created/updated, we have to clear the cache, so users can see new data. and to do this we will tweak our middleware code a bit. so in the part where we check the request method we add this:
if ('GET' !== $method) {
$response = $next($request);
if ($response->isSuccessful()) {
$tag = $request->url();
if ('PATCH' === $method || 'DELETE' === $method) {
$tag = mb_substr($tag, 0, mb_strrpos($tag, '/'));
}
cache()->tags([$tag])->flush();
}
return $response;
}
So what this code is doing is flushing the cache for non-GET requests. Then for PATCH and Delete requests we are stripping the {id}. so for example if the request url is PATCH /users/1/posts/2 . We are stripping the last id leaving /users/1/posts. this way when we update a post, we clear the cache of all a users posts. so the user can see fresh data.
Now with this we are done with the CacheLayer implementation. Lets test it
Testing our Cache
Let's say we want to retrieve all a users posts, that has links, media and sort it by likes and recently created. the url for that kind of request according to the json:api spec will look like: /posts?filter[links]=1&filter[media]=1&sort=-created_at,-likes. on a posts table of 1.2 million records the response time is: ~800ms
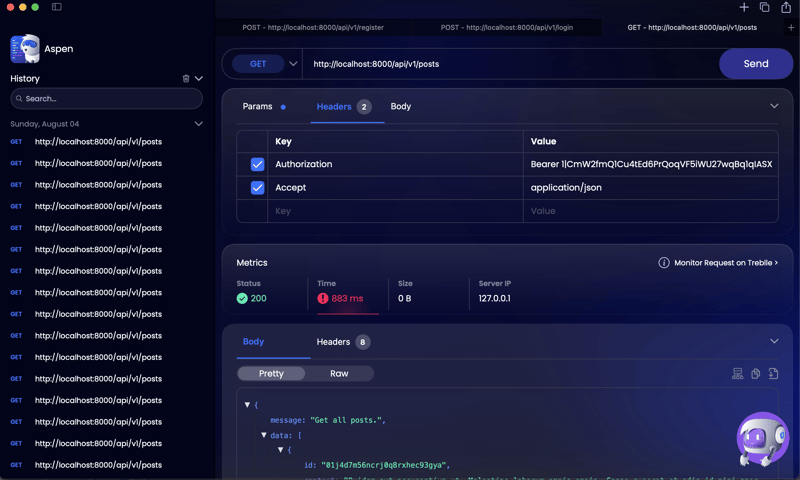
and after adding our cache middleware we get a response time of 41ms
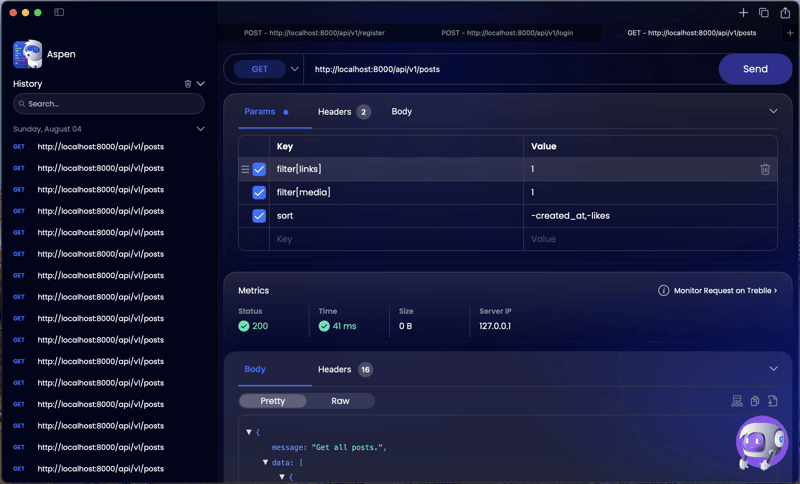
Great success!
Optimizations
Another optional step is to compress the json payload we store on redis. JSON is not the most memory-efficient format, so what we can do is use zlib compression to compress the json before storing and decompress before sending to the client.
the code for that will look like:
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return gzcompress($res->getContent());
}
);
return $exception ?? response(gzuncompress($response));
The full code for this looks like:
getMethod();
if ('GET' !== $method) {
$response = $next($request);
if ($response->isSuccessful()) {
$tag = $request->url();
if ('PATCH' === $method || 'DELETE' === $method) {
$tag = mb_substr($tag, 0, mb_strrpos($tag, '/'));
}
cache()->tags([$tag])->flush();
}
return $response;
}
foreach (self::EXCLUDED_URLS as $pattern) {
if (preg_match($pattern, $request->getRequestUri())) {
return $next($request);
}
}
$cacheKey = $this->getCacheKey($request);
$exception = null;
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return gzcompress($res->getContent());
}
);
return $exception ?? response(gzuncompress($response));
}
private function getCacheKey(Request $request): string
{
$routeParameters = ! empty($request->route()->parameters) ? $request->route()->parameters : [auth()->user()->id];
$allParameters = array_merge($request->all(), $routeParameters);
$this->recursiveSort($allParameters);
return $request->url() . json_encode($allParameters);
}
private function recursiveSort(&$array): void
{
foreach ($array as &$value) {
if (is_array($value)) {
$this->recursiveSort($value);
}
}
ksort($array);
}
}
Summary
This is all I have for you today on caching, Happy building and drop any questions, commments and improvements in the comments!
-
 如何將MySQL數據庫添加到Visual Studio 2012中的數據源對話框中?在Visual Studio 2012 儘管已安裝了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但無法將MySQL數據庫添加到實體框架的“ DataSource對話框”中。為了解決這一問題,至關重要的是要了解MySQL連接器v.6.5.5及以後的6.6.x版本將提供MySQL的官方Visual...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
如何將MySQL數據庫添加到Visual Studio 2012中的數據源對話框中?在Visual Studio 2012 儘管已安裝了MySQL Connector v.6.5.4,但無法將MySQL數據庫添加到實體框架的“ DataSource對話框”中。為了解決這一問題,至關重要的是要了解MySQL連接器v.6.5.5及以後的6.6.x版本將提供MySQL的官方Visual...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 如何處理PHP文件系統功能中的UTF-8文件名?在PHP的Filesystem functions中處理UTF-8 FileNames 在使用PHP的MKDIR函數中含有UTF-8字符的文件很多flusf-8字符時,您可能會在Windows Explorer中遇到comploreer grounder grounder grounder gro...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
如何處理PHP文件系統功能中的UTF-8文件名?在PHP的Filesystem functions中處理UTF-8 FileNames 在使用PHP的MKDIR函數中含有UTF-8字符的文件很多flusf-8字符時,您可能會在Windows Explorer中遇到comploreer grounder grounder grounder gro...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 Python元類工作原理及類創建與定制python中的metaclasses是什麼? Metaclasses負責在Python中創建類對象。就像類創建實例一樣,元類也創建類。他們提供了對類創建過程的控制層,允許自定義類行為和屬性。 在Python中理解類作為對象的概念,類是描述用於創建新實例或對象的藍圖的對象。這意味著類本身是使用...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
Python元類工作原理及類創建與定制python中的metaclasses是什麼? Metaclasses負責在Python中創建類對象。就像類創建實例一樣,元類也創建類。他們提供了對類創建過程的控制層,允許自定義類行為和屬性。 在Python中理解類作為對象的概念,類是描述用於創建新實例或對象的藍圖的對象。這意味著類本身是使用...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data編碼使用其他參數上傳文件?使用http request 上傳文件上傳到http server,同時也提交其他參數,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data編碼使用其他參數上傳文件?使用http request 上傳文件上傳到http server,同時也提交其他參數,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 Java的Map.Entry和SimpleEntry如何簡化鍵值對管理?的綜合集合:在Java中介紹Java的Map.entry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry apry and Map。 地圖。它具有兩個通用...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
Java的Map.Entry和SimpleEntry如何簡化鍵值對管理?的綜合集合:在Java中介紹Java的Map.entry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry和SimpleEntry apry and Map。 地圖。它具有兩個通用...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 您如何在Laravel Blade模板中定義變量?在Laravel Blade模板中使用Elegance 在blade模板中如何分配變量對於存儲以後使用的數據至關重要。在使用“ {{}}”分配變量的同時,它可能並不總是最優雅的解決方案。 幸運的是,Blade通過@php Directive提供了更優雅的方法: $ old_section =...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
您如何在Laravel Blade模板中定義變量?在Laravel Blade模板中使用Elegance 在blade模板中如何分配變量對於存儲以後使用的數據至關重要。在使用“ {{}}”分配變量的同時,它可能並不總是最優雅的解決方案。 幸運的是,Blade通過@php Directive提供了更優雅的方法: $ old_section =...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 Android如何向PHP服務器發送POST數據?在android apache httpclient(已棄用) httpclient httpclient = new defaulthttpclient(); httppost httppost = new httppost(“ http://www.yoursite.com/script.p...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
Android如何向PHP服務器發送POST數據?在android apache httpclient(已棄用) httpclient httpclient = new defaulthttpclient(); httppost httppost = new httppost(“ http://www.yoursite.com/script.p...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 Java字符串非空且非null的有效檢查方法檢查字符串是否不是null而不是空的 if(str!= null && str.isementy())二手: if(str!= null && str.length()== 0) option 3:trim()。 isement(Isement() trim whitespace whites...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
Java字符串非空且非null的有效檢查方法檢查字符串是否不是null而不是空的 if(str!= null && str.isementy())二手: if(str!= null && str.length()== 0) option 3:trim()。 isement(Isement() trim whitespace whites...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 如何在Chrome中居中選擇框文本?選擇框的文本對齊:局部chrome-inly-ly-ly-lyly solument 您可能希望將文本中心集中在選擇框中,以獲取優化的原因或提高可訪問性。但是,在CSS中的選擇元素中手動添加一個文本 - 對屬性可能無法正常工作。 初始嘗試 state)</option> < o...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
如何在Chrome中居中選擇框文本?選擇框的文本對齊:局部chrome-inly-ly-ly-lyly solument 您可能希望將文本中心集中在選擇框中,以獲取優化的原因或提高可訪問性。但是,在CSS中的選擇元素中手動添加一個文本 - 對屬性可能無法正常工作。 初始嘗試 state)</option> < o...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 解決Spring Security 4.1及以上版本CORS問題指南彈簧安全性cors filter:故障排除常見問題 在將Spring Security集成到現有項目中時,您可能會遇到與CORS相關的錯誤,如果像“訪問Control-allo-allow-Origin”之類的標頭,則無法設置在響應中。為了解決此問題,您可以實現自定義過濾器,例如代碼段中的MyFi...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
解決Spring Security 4.1及以上版本CORS問題指南彈簧安全性cors filter:故障排除常見問題 在將Spring Security集成到現有項目中時,您可能會遇到與CORS相關的錯誤,如果像“訪問Control-allo-allow-Origin”之類的標頭,則無法設置在響應中。為了解決此問題,您可以實現自定義過濾器,例如代碼段中的MyFi...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 在PHP中如何高效檢測空數組?在PHP 中檢查一個空數組可以通過各種方法在PHP中確定一個空數組。如果需要驗證任何數組元素的存在,則PHP的鬆散鍵入允許對數組本身進行直接評估:一種更嚴格的方法涉及使用count()函數: if(count(count($ playerList)=== 0){ //列表為空。 } 對...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
在PHP中如何高效檢測空數組?在PHP 中檢查一個空數組可以通過各種方法在PHP中確定一個空數組。如果需要驗證任何數組元素的存在,則PHP的鬆散鍵入允許對數組本身進行直接評估:一種更嚴格的方法涉及使用count()函數: if(count(count($ playerList)=== 0){ //列表為空。 } 對...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08 -
 Python中何時用"try"而非"if"檢測變量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”來測試python 在python中的變量值,在某些情況下,您可能需要在處理之前檢查變量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”構建體之間決定。 “ if” constructs result = function() 如果結果: 對於結果: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
Python中何時用"try"而非"if"檢測變量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”來測試python 在python中的變量值,在某些情況下,您可能需要在處理之前檢查變量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”構建體之間決定。 “ if” constructs result = function() 如果結果: 對於結果: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-05-08
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























