이동 시간 및 기간 | 프로그래밍 튜토리얼
2024-11-02에 게시됨
소개
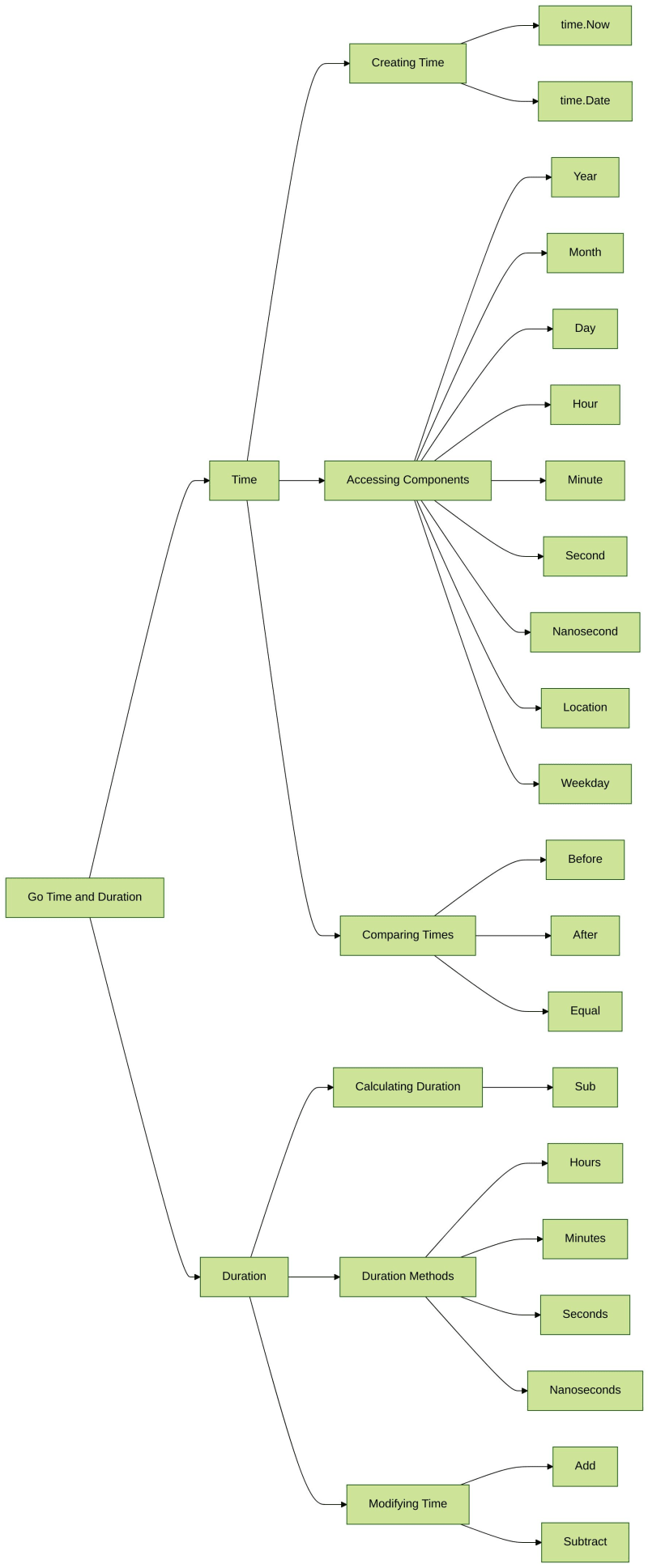
이 랩의 목표는 Go의 시간 및 기간 지원에 대한 이해도를 테스트하는 것입니다.
시간
아래 코드에는 Go에서 시간과 기간을 사용하는 방법에 대한 예가 포함되어 있습니다. 그러나 코드의 일부가 누락되었습니다. 귀하의 임무는 예상대로 작동하도록 코드를 완성하는 것입니다.
- Go 프로그래밍 언어에 대한 기본 지식
- Go의 시간 및 기간 지원에 대해 잘 알고 있습니다.
$ go run time.go 2012-10-31 15:50:13.793654 0000 UTC 2009-11-17 20:34:58.651387237 0000 UTC 2009 November 17 20 34 58 651387237 UTC Tuesday true false false 25891h15m15.142266763s 25891.25420618521 1.5534752523711128e 06 9.320851514226677e 07 93208515142266763 2012-10-31 15:50:13.793654 0000 UTC 2006-12-05 01:19:43.509120474 0000 UTC # Next we'll look at the related idea of time relative to # the Unix epoch.
아래에 전체 코드가 있습니다.
// Go offers extensive support for times and durations;
// here are some examples.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
p := fmt.Println
// We'll start by getting the current time.
now := time.Now()
p(now)
// You can build a `time` struct by providing the
// year, month, day, etc. Times are always associated
// with a `Location`, i.e. time zone.
then := time.Date(
2009, 11, 17, 20, 34, 58, 651387237, time.UTC)
p(then)
// You can extract the various components of the time
// value as expected.
p(then.Year())
p(then.Month())
p(then.Day())
p(then.Hour())
p(then.Minute())
p(then.Second())
p(then.Nanosecond())
p(then.Location())
// The Monday-Sunday `Weekday` is also available.
p(then.Weekday())
// These methods compare two times, testing if the
// first occurs before, after, or at the same time
// as the second, respectively.
p(then.Before(now))
p(then.After(now))
p(then.Equal(now))
// The `Sub` methods returns a `Duration` representing
// the interval between two times.
diff := now.Sub(then)
p(diff)
// We can compute the length of the duration in
// various units.
p(diff.Hours())
p(diff.Minutes())
p(diff.Seconds())
p(diff.Nanoseconds())
// You can use `Add` to advance a time by a given
// duration, or with a `-` to move backwards by a
// duration.
p(then.Add(diff))
p(then.Add(-diff))
}
요약
이 실습에서는 Go의 시간 및 기간 지원 작업 능력을 테스트했습니다. 시간 값의 다양한 구성요소를 추출하고, 두 시간을 비교하고, 기간의 길이를 계산하고, 주어진 기간만큼 시간을 앞당기는 방법을 배웠습니다.
? 지금 연습하세요: 이동 시간 및 기간 탐색
더 자세히 알고 싶으십니까?
- ? 최신 바둑 스킬 트리를 알아보세요
- ? 더 많은 Go 튜토리얼을 읽어보세요
- ? Discord에 참여하거나 @WeAreLabEx로 트윗해 주세요.
릴리스 선언문
이 글은 https://dev.to/labex/go-time-and-duration-programming-tutorials-786?1에서 복제됩니다.1 침해 내용이 있는 경우, [email protected]으로 연락하여 삭제하시기 바랍니다.
최신 튜토리얼
더>
-
 열의 열이 다른 데이터베이스 테이블을 어떻게 통합하려면 어떻게해야합니까?다른 열이있는 결합 테이블 ] 는 데이터베이스 테이블을 다른 열로 병합하려고 할 때 도전에 직면 할 수 있습니다. 간단한 방법은 열이 적은 테이블의 누락 된 열에 null 값을 추가하는 것입니다. 예를 들어, 표 B보다 더 많은 열이있는 두 개의 테이블,...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
열의 열이 다른 데이터베이스 테이블을 어떻게 통합하려면 어떻게해야합니까?다른 열이있는 결합 테이블 ] 는 데이터베이스 테이블을 다른 열로 병합하려고 할 때 도전에 직면 할 수 있습니다. 간단한 방법은 열이 적은 테이블의 누락 된 열에 null 값을 추가하는 것입니다. 예를 들어, 표 B보다 더 많은 열이있는 두 개의 테이블,...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 교체 지시문을 사용하여 GO MOD에서 모듈 경로 불일치를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?[ github.com/coreos/coreos/client github.com/coreos/etcd/client.test imports github.com/coreos/etcd/integration에 의해 테스트 된 Echoed 메시지에 의해 입증 된 바와...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
교체 지시문을 사용하여 GO MOD에서 모듈 경로 불일치를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?[ github.com/coreos/coreos/client github.com/coreos/etcd/client.test imports github.com/coreos/etcd/integration에 의해 테스트 된 Echoed 메시지에 의해 입증 된 바와...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 크롬에서 상자 텍스트를 선택하는 방법은 무엇입니까?초기 시도 한 가지 일반적인 접근 방식은 다음과 같습니다. 주) & lt;/옵션 & gt; & lt; 옵션> select .lt {text-align : center; } <option value=""&a...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
크롬에서 상자 텍스트를 선택하는 방법은 무엇입니까?초기 시도 한 가지 일반적인 접근 방식은 다음과 같습니다. 주) & lt;/옵션 & gt; & lt; 옵션> select .lt {text-align : center; } <option value=""&a...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 익명의 JavaScript 이벤트 처리기를 깨끗하게 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?익명 이벤트 리스너를 제거하는 데 익명의 이벤트 리스너 추가 요소를 추가하면 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만, 그것들을 제거 할 시간이되면, 요소 자체를 교체하지 않고 도전 할 수 있습니다. 요소? element.addevent...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
익명의 JavaScript 이벤트 처리기를 깨끗하게 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?익명 이벤트 리스너를 제거하는 데 익명의 이벤트 리스너 추가 요소를 추가하면 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만, 그것들을 제거 할 시간이되면, 요소 자체를 교체하지 않고 도전 할 수 있습니다. 요소? element.addevent...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 FormData ()로 여러 파일 업로드를 처리하려면 어떻게해야합니까?); 그러나이 코드는 첫 번째 선택된 파일 만 처리합니다. 파일 : var files = document.getElementById ( 'filetOUpload'). 파일; for (var x = 0; x프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
FormData ()로 여러 파일 업로드를 처리하려면 어떻게해야합니까?); 그러나이 코드는 첫 번째 선택된 파일 만 처리합니다. 파일 : var files = document.getElementById ( 'filetOUpload'). 파일; for (var x = 0; x프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 Fastapi Custom 404 페이지 제작 가이드custom 404 fastapi 가없는 페이지를 찾을 수 없습니다. 적절한 방법은 특정 요구 사항에 따라 다릅니다. 404 상태 코드에서 리디렉션 response = await call_next(request) if response.sta...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
Fastapi Custom 404 페이지 제작 가이드custom 404 fastapi 가없는 페이지를 찾을 수 없습니다. 적절한 방법은 특정 요구 사항에 따라 다릅니다. 404 상태 코드에서 리디렉션 response = await call_next(request) if response.sta...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 선형 구배 배경에 줄무늬가있는 이유는 무엇이며 어떻게 고칠 수 있습니까?수직 지향적 구배의 경우, 신체 요소의 마진은 HTML 요소로 전파되어 8px 키가 큰 영역을 초래합니다. 그 후, 선형 등급은이 전체 높이에 걸쳐 확장되어 반복 패턴을 생성합니다. 솔루션 : 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 신체 요소에 충분한 높이가 있는지 ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
선형 구배 배경에 줄무늬가있는 이유는 무엇이며 어떻게 고칠 수 있습니까?수직 지향적 구배의 경우, 신체 요소의 마진은 HTML 요소로 전파되어 8px 키가 큰 영역을 초래합니다. 그 후, 선형 등급은이 전체 높이에 걸쳐 확장되어 반복 패턴을 생성합니다. 솔루션 : 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 신체 요소에 충분한 높이가 있는지 ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 오른쪽 테이블의 where 조항에서 필터링 할 때 왼쪽 결합이 연결된 이유는 무엇입니까?다음 쿼리를 상상해보십시오 : select A.Foo, B. 바, c.foobar a로 테이블온에서 내부는 a.pk = b.fk에서 b로 tabletwo를 결합합니다 b.pk = c.fk에서 c as c로 왼쪽으로 결합하십시오 여기서 a.foo = '...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
오른쪽 테이블의 where 조항에서 필터링 할 때 왼쪽 결합이 연결된 이유는 무엇입니까?다음 쿼리를 상상해보십시오 : select A.Foo, B. 바, c.foobar a로 테이블온에서 내부는 a.pk = b.fk에서 b로 tabletwo를 결합합니다 b.pk = c.fk에서 c as c로 왼쪽으로 결합하십시오 여기서 a.foo = '...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 PYTZ가 처음에 예상치 못한 시간대 오프셋을 표시하는 이유는 무엇입니까?import pytz pytz.timezone ( 'Asia/Hong_kong') std> discrepancy source 역사 전반에 걸쳐 변동합니다. PYTZ가 제공하는 기본 시간대 이름 및 오프...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
PYTZ가 처음에 예상치 못한 시간대 오프셋을 표시하는 이유는 무엇입니까?import pytz pytz.timezone ( 'Asia/Hong_kong') std> discrepancy source 역사 전반에 걸쳐 변동합니다. PYTZ가 제공하는 기본 시간대 이름 및 오프...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 팬더에서 연도와 1/4 열을 하나의주기적인 열로 병합하는 방법은 무엇입니까?새로운 기간 열에 대한 열을 연결하는 열 문제 문 : 라는 열이있는 pandas dataframe을 고려하십시오 : 분기 2000 Q2 2001 Q3 목표는 다음과 같은 결과를 얻기 위해 "연도"...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
팬더에서 연도와 1/4 열을 하나의주기적인 열로 병합하는 방법은 무엇입니까?새로운 기간 열에 대한 열을 연결하는 열 문제 문 : 라는 열이있는 pandas dataframe을 고려하십시오 : 분기 2000 Q2 2001 Q3 목표는 다음과 같은 결과를 얻기 위해 "연도"...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 동적 인 크기의 부모 요소 내에서 요소의 스크롤 범위를 제한하는 방법은 무엇입니까?문제 : 고정 된 사이드 바로 조정을 유지하면서 사용자의 수직 스크롤과 함께 이동하는 스크롤 가능한 맵 디브가있는 레이아웃을 고려합니다. 그러나 맵의 스크롤은 뷰포트의 높이를 초과하여 사용자가 페이지 바닥 글에 액세스하는 것을 방지합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
동적 인 크기의 부모 요소 내에서 요소의 스크롤 범위를 제한하는 방법은 무엇입니까?문제 : 고정 된 사이드 바로 조정을 유지하면서 사용자의 수직 스크롤과 함께 이동하는 스크롤 가능한 맵 디브가있는 레이아웃을 고려합니다. 그러나 맵의 스크롤은 뷰포트의 높이를 초과하여 사용자가 페이지 바닥 글에 액세스하는 것을 방지합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 MySQLI로 전환 한 후 Codeigniter가 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결 해야하는 이유문제를 디버깅하려면 파일 끝에 다음 코드를 추가하고 출력을 검토하는 것이 좋습니다. echo ''; print_r ($ db ); echo ''; echo '데이터베이스에 연결 :'. $ db ; $ dbh = mysq...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
MySQLI로 전환 한 후 Codeigniter가 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결 해야하는 이유문제를 디버깅하려면 파일 끝에 다음 코드를 추가하고 출력을 검토하는 것이 좋습니다. echo ''; print_r ($ db ); echo ''; echo '데이터베이스에 연결 :'. $ db ; $ dbh = mysq...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 Firefox Back 버튼을 사용할 때 JavaScript 실행이 중단되는 이유는 무엇입니까?원인 및 솔루션 : 이 동작은 브라우저 캐싱 자바 스크립트 리소스에 의해 발생합니다. 이 문제를 해결하고 후속 페이지 방문에서 스크립트가 실행되도록하기 위해 Firefox 사용자는 Window.onload 이벤트에서 호출되도록 빈 기능을 설정해야합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
Firefox Back 버튼을 사용할 때 JavaScript 실행이 중단되는 이유는 무엇입니까?원인 및 솔루션 : 이 동작은 브라우저 캐싱 자바 스크립트 리소스에 의해 발생합니다. 이 문제를 해결하고 후속 페이지 방문에서 스크립트가 실행되도록하기 위해 Firefox 사용자는 Window.onload 이벤트에서 호출되도록 빈 기능을 설정해야합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 `JSON '패키지를 사용하여 이동하는 JSON 어레이를 구문 분석하는 방법은 무엇입니까?JSON 어레이를 Parsing JSON 패키지 문제 : JSON 패키지를 사용하여 어레이를 나타내는 JSON 스트링을 어떻게 구문 분석 할 수 있습니까? 예 : type JsonType struct { Array []string ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
`JSON '패키지를 사용하여 이동하는 JSON 어레이를 구문 분석하는 방법은 무엇입니까?JSON 어레이를 Parsing JSON 패키지 문제 : JSON 패키지를 사용하여 어레이를 나타내는 JSON 스트링을 어떻게 구문 분석 할 수 있습니까? 예 : type JsonType struct { Array []string ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다 -
 McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 암호화를 마이그레이션하고 OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRypt 암호화 데이터를 해제 할 수 있습니까?질문 : McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 내 암호화 라이브러리를 업그레이드 할 수 있습니까? 그렇다면 어떻게? 대답 : 대답 : 예, McRypt에서 암호화 라이브러리를 OpenSSL로 업그레이드 할 수 있습니다. OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRyp...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 암호화를 마이그레이션하고 OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRypt 암호화 데이터를 해제 할 수 있습니까?질문 : McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 내 암호화 라이브러리를 업그레이드 할 수 있습니까? 그렇다면 어떻게? 대답 : 대답 : 예, McRypt에서 암호화 라이브러리를 OpenSSL로 업그레이드 할 수 있습니다. OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRyp...프로그램 작성 2025-07-01에 게시되었습니다
중국어 공부
- 1 "걷다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 走路 중국어 발음, 走路 중국어 학습
- 2 "비행기를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐飞机 중국어 발음, 坐飞机 중국어 학습
- 3 "기차를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐火车 중국어 발음, 坐火车 중국어 학습
- 4 "버스를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐车 중국어 발음, 坐车 중국어 학습
- 5 운전을 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 开车 중국어 발음, 开车 중국어 학습
- 6 수영을 중국어로 뭐라고 하나요? 游泳 중국어 발음, 游泳 중국어 학습
- 7 자전거를 타다 중국어로 뭐라고 하나요? 骑自行车 중국어 발음, 骑自行车 중국어 학습
- 8 중국어로 안녕하세요를 어떻게 말해요? 你好중국어 발음, 你好중국어 학습
- 9 감사합니다를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 谢谢중국어 발음, 谢谢중국어 학습
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























