Deep dive into Array Data Structure
Published on 2024-09-02
What is an Array?
- Array is a collection of elements, each identified by an index or key.
- Arrays have a fixed & dynamic size
- Homogeneous elements → all elements in an array are of the same data type.
- Heterogeneous elements → allowing different data types in the same array.
// Homogeneous int[] intArray = new int[5]; // Array of integers String[] stringArray = new String[5]; // Array of strings // Heterogeneous mixedArray = [1, "hello", 3.14, True] # Mixed data types in one list
Characteristics of Arrays
- Indexing: Zero-based indexing in most programming languages.
- Size: Fixed size (static), cannot be changed dynamically (except in languages with dynamic arrays).
- Memory Allocation: Contiguous memory allocation for array elements. meaning each element is directly next to the previous one in memory. This is possible because all elements are of the same size, allowing the system to calculate the memory address of any element using its index.
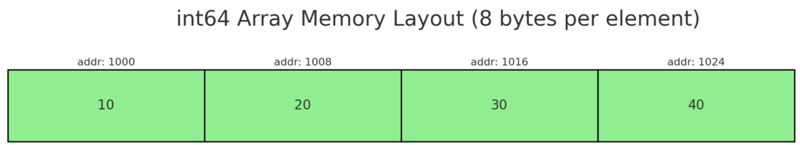
Array Operations
- Insertion: Typically involves shifting elements, O(n) time complexity.
- Deletion: Similar to insertion, elements may need to be shifted. Except last index
- Traversal: Iterating through all elements, O(n) time complexity.
- Access Time: O(1) time complexity for accessing an element using its index.
Types of Arrays
- One-dimensional Array: Simplest form, like a list.
- Multi-dimensional Array: Arrays of arrays (e.g., 2D array).
- Jagged Array: Arrays with different lengths of sub-arrays.
- Dynamic Arrays (e.g., ArrayList in Java): Arrays that can grow in size dynamically.
Advantages of Arrays
- Efficiency: O(1) access time for elements.
- Memory Utilization: Efficient use of memory due to contiguous storage.
- Ease of Use: Simplifies data management and operations like sorting and searching
Disadvantages of Arrays
- Fixed Size: Cannot change size once declared. except dynamic array
- Insertion/Deletion Cost: O(n) for inserting or deleting an element, especially in the middle.
- Memory Wastage: Unused elements still occupy space.
Real-world Applications of Arrays
- Storing Data: Common in programming for storing collections of elements.
- Sorting Algorithms: Many sorting algorithms are designed for arrays (e.g., QuickSort, MergeSort).
- Matrix Operations: 2D arrays are used for matrix operations in mathematics and graphics.
- Implementing Stacks and Queues: Basic data structures can be implemented using arrays.
Best Practices with Arrays
- Avoid Unnecessary Copies: Be mindful of operations that require copying elements.
- Use Dynamic Arrays When Needed: If size is uncertain, prefer dynamic arrays.
- Leverage Built-in Functions: Utilize language-specific functions for array operations.
- Boundary Checking: Always check for boundary conditions to avoid IndexOutOfBoundsException.
Static & Dynamic Array example in GO
package main
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
// Static Array
var staticArr [5]int64
staticArr[0] = 1
staticArr[1] = 2
staticArr[2] = 3
staticArr[3] = 4
staticArr[4] = 5
elementSize := unsafe.Sizeof(staticArr[0])
totalSize := elementSize * uintptr(len(staticArr))
fmt.Printf("Memory used by static array: %d bytes\n", totalSize)
fmt.Println()
// Dynamic Array (Slice)
dynamicArr := make([]int32, 0, 5)
before := unsafe.Sizeof(dynamicArr[0])
beforeTotal := before * uintptr(len(dynamicArr))
fmt.Printf("Memory used by dynamic array (before): %d bytes\n", beforeTotal)
// Append elements to dynamic array
for i := 0; i
Release Statement
This article is reproduced at: https://dev.to/chandra179/deep-dive-into-array-data-structure-1g82?1 If there is any infringement, please contact [email protected] to delete it
Latest tutorial
More>
-
 User local time format and time zone offset display guideDisplaying Date/Time in User's Locale Format with Time OffsetWhen presenting dates and times to end-users, it's crucial to display them in the...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
User local time format and time zone offset display guideDisplaying Date/Time in User's Locale Format with Time OffsetWhen presenting dates and times to end-users, it's crucial to display them in the...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How do Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntry simplify key-value pair management?A Comprehensive Collection for Value Pairs: Introducing Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntryIn Java, when defining a collection where each element com...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How do Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntry simplify key-value pair management?A Comprehensive Collection for Value Pairs: Introducing Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntryIn Java, when defining a collection where each element com...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 `console.log` shows the reason for the modified object value exceptionObjects and Console.log: An Oddity UnraveledWhen working with objects and console.log, you may encounter peculiar behavior. Let's unravel this mys...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
`console.log` shows the reason for the modified object value exceptionObjects and Console.log: An Oddity UnraveledWhen working with objects and console.log, you may encounter peculiar behavior. Let's unravel this mys...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to pass exclusive pointers as function or constructor parameters in C++?Managing Unique Pointers as Parameters in Constructors and FunctionsUnique pointers (unique_ptr) uphold the principle of unique ownership in C 11. Wh...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to pass exclusive pointers as function or constructor parameters in C++?Managing Unique Pointers as Parameters in Constructors and FunctionsUnique pointers (unique_ptr) uphold the principle of unique ownership in C 11. Wh...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to prevent duplicate submissions after form refresh?Preventing Duplicate Submissions with Refresh HandlingIn web development, it's common to encounter the issue of duplicate submissions when a page ...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to prevent duplicate submissions after form refresh?Preventing Duplicate Submissions with Refresh HandlingIn web development, it's common to encounter the issue of duplicate submissions when a page ...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to Efficiently Convert Timezones in PHP?Efficient Timezone Conversion in PHPIn PHP, handling timezones can be a straightforward task. This guide will provide an easy-to-implement method for ...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to Efficiently Convert Timezones in PHP?Efficient Timezone Conversion in PHPIn PHP, handling timezones can be a straightforward task. This guide will provide an easy-to-implement method for ...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 Tips for finding element position in Java arrayRetrieving Element Position in Java ArraysWithin Java's Arrays class, there is no direct "indexOf" method to determine the position of a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Tips for finding element position in Java arrayRetrieving Element Position in Java ArraysWithin Java's Arrays class, there is no direct "indexOf" method to determine the position of a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 How to deal with sliced memory in Go language garbage collection?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array. When working with slices, i...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
How to deal with sliced memory in Go language garbage collection?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array. When working with slices, i...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 Method for correct passing of C++ member function pointersHow to Pass Member Function Pointers in C When passing a class member function to a function that accepts a member function pointer, it's essenti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Method for correct passing of C++ member function pointersHow to Pass Member Function Pointers in C When passing a class member function to a function that accepts a member function pointer, it's essenti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 Tips for floating pictures to the right side of the bottom and wrapping around textFloating an Image to the Bottom Right with Text Wrapping AroundIn web design, it is sometimes desirable to float an image to the bottom right corner o...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Tips for floating pictures to the right side of the bottom and wrapping around textFloating an Image to the Bottom Right with Text Wrapping AroundIn web design, it is sometimes desirable to float an image to the bottom right corner o...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18 -
 Solve the \\"String value error\\" exception when MySQL inserts EmojiResolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Solve the \\"String value error\\" exception when MySQL inserts EmojiResolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...Programming Posted on 2025-07-18
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























